Page 490 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 490
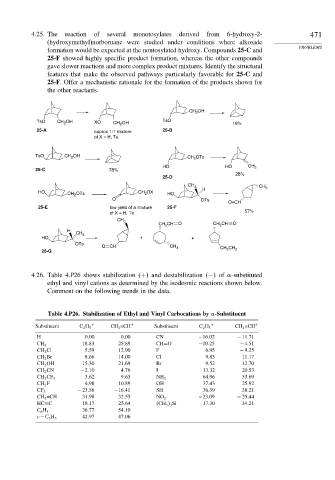
4.25. The reaction of several monotosylates derived from 6-hydroxy-2- 471
(hydroxymethyl)norbornane were studied under conditions where alkoxide
PROBLEMS
formation would be expected at the nontosylated hydroxy. Compounds 25-C and
25-F showed highly specific product formation, whereas the other compounds
gave slower reactions and more complex product mixtures. Identify the structural
features that make the observed pathways particularly favorable for 25-C and
25-F. Offer a mechanistic rationale for the formation of the products shown for
the other reactants.
CH OH
2
TsO CH OH XO CH 2 OH TsO 19%
2
25-A 25-B
approx 1:1 mixture
of X = H, Ts
TsO CH 2 OH CH 2 OTs
HO HO CH
25-C 78% 2
28%
25-D
CH 3 CH
HO OTs CH OX H 3
CH 2 2 HO
O OTs
O=CH
25-E low yield of a mixture 25-F
of X = H, Ts 57%
CH 3
CH 2 CH O CH CH O
2
H
CH 3
HO + +
OTs
O CH CH 3 CH
25-G CH 2 3
4.26. Table 4.P26 shows stabilization + and destabilization − of
-substituted
ethyl and vinyl cations as determined by the isodesmic reactions shown below.
Comment on the following trends in the data.
Table 4.P26. Stabilization of Ethyl and Vinyl Carbocations by
-Substituent
Substituent C 2 H 5 + CH 2 =CH + Substituent C 2 H 5 + CH 2 =CH +
H 0 00 0 00 CN −16 02 −11 71
18 83 25 89 CH=O −10 25 −4 51
CH 3
CH 2 Cl 5 59 12 90 F 6.95 −9 25
CH 2 Br 8 66 14 00 Cl 9.83 11 17
CH 2 OH 15 30 21 69 Br 9.52 12 70
CH 2 CN −2 10 4 76 I 13.32 20 53
3 62 9 63 64.96 53 69
CH 2 CF 3 NH 2
CH 2 F 4 98 10 89 OH 37.43 25 92
−23 56 −16 41 SH 36.39 38 21
CF 3
CH 2 =CH 31 98 32 55 NO 2 −23 09 −25 44
HC≡C 18 17 25 64 CH 3 3 Si 17.30 34 21
36 77 54 10
C 6 H 5
42 97 47 06
c −C 3 H 5