Page 488 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 488
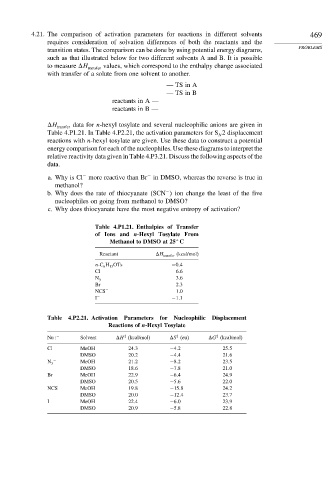
4.21. The comparison of activation parameters for reactions in different solvents 469
requires consideration of solvation differences of both the reactants and the
transition states. The comparison can be done by using potential energy diagrams, PROBLEMS
such as that illustrated below for two different solvents A and B. It is possible
to measure H transfer values, which correspond to the enthalpy change associated
with transfer of a solute from one solvent to another.
—TSinA
—TSinB
reactants in A —
reactants in B —
H transfer data for n-hexyl tosylate and several nucleophilic anions are given in
Table 4.P1.21. In Table 4.P2.21, the activation parameters for S 2 displacement
N
reactions with n-hexyl tosylate are given. Use these data to construct a potential
energy comparison for each of the nucleophiles. Use these diagrams to interpret the
relative reactivity data given in Table 4.P3.21. Discuss the following aspects of the
data.
a. Why is Cl more reactive than Br in DMSO, whereas the reverse is true in
−
−
methanol?
b. Why does the rate of thiocyanate SCN ion change the least of the five
−
nucleophiles on going from methanol to DMSO?
c. Why does thiocyanate have the most negative entropy of activation?
Table 4.P1.21. Enthalpies of Transfer
of Ions and n-Hexyl Tosylate From
Methanol to DMSO at 25 C
Reactant H transfer (kcal/mol)
n-C 6 H 13 OTs −0 4
Cl − 6.6
N − 3.6
3
Br − 2.3
NCS − 1.0
I − −1 1
Table 4.P2.21. Activation Parameters for Nucleophilic Displacement
Reactions of n-Hexyl Tosylate
‡
‡
‡
Nu − Solvent H (kcal/mol) S (eu) G (kcal/mol)
Cl − MeOH 24 3 −4 2 25 5
DMSO 20 2 −4 4 21 6
− MeOH 21 2 −8 2 23 5
N 3
DMSO 18 6 −7 8 21 0
Br − MeOH 22 9 −6 4 24 9
DMSO 20 5 −5 6 22 0
NCS − MeOH 19 8 −15 8 24 2
DMSO 20 0 −12 4 23 7
I − MeOH 22 4 −6 0 23 9
DMSO 20 9 −5 8 22 8