Page 510 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 510
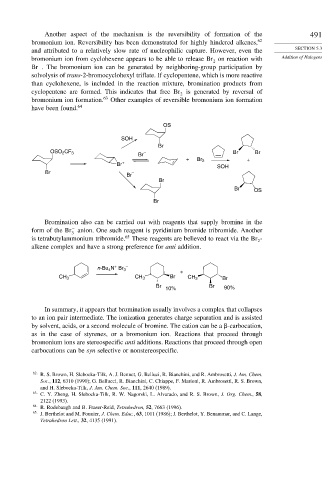
Another aspect of the mechanism is the reversibility of formation of the 491
bromonium ion. Reversibility has been demonstrated for highly hindered alkenes, 62
and attributed to a relatively slow rate of nucleophilic capture. However, even the SECTION 5.3
bromonium ion from cyclohexene appears to be able to release Br on reaction with Addition of Halogens
2
−
Br . The bromonium ion can be generated by neighboring-group participation by
solvolysis of trans-2-bromocyclohexyl triflate. If cyclopentene, which is more reactive
than cyclohexene, is included in the reaction mixture, bromination products from
cyclopentene are formed. This indicates that free Br is generated by reversal of
2
bromonium ion formation. 63 Other examples of reversible bromonium ion formation
have been found. 64
OS
SOH
Br
OSO 2 CF 3 – Br Br
Br
+ Br 2 +
Br +
SOH
Br –
Br
Br
Br OS
Br
Bromination also can be carried out with reagents that supply bromine in the
−
form of the Br anion. One such reagent is pyridinium bromide tribromide. Another
3
is tetrabutylammonium tribromide. 65 These reagents are believed to react via the Br -
2
alkene complex and have a strong preference for anti addition.
+
n-Bu N Br 3 – +
4
Br
CH 3 CH 3 CH 3 Br
Br 10% Br 90%
In summary, it appears that bromination usually involves a complex that collapses
to an ion pair intermediate. The ionization generates charge separation and is assisted
by solvent, acids, or a second molecule of bromine. The cation can be a -carbocation,
as in the case of styrenes, or a bromonium ion. Reactions that proceed through
bromonium ions are stereospecific anti additions. Reactions that proceed through open
carbocations can be syn selective or nonstereospecific.
62
R. S. Brown, H. Slebocka-Tilk, A. J. Bennet, G. Belluci, R. Bianchini, and R. Ambrosetti, J. Am. Chem.
Soc., 112, 6310 (1990); G. Bellucci, R. Bianchini, C. Chiappe, F. Marioni, R. Ambrosetti, R. S. Brown,
and H. Slebocka-Tilk, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 111, 2640 (1989).
63 C. Y. Zheng, H. Slebocka-Tilk, R. W. Nagorski, L. Alvarado, and R. S. Brown, J. Org. Chem., 58,
2122 (1993).
64 R. Rodebaugh and B. Fraser-Reid, Tetrahedron, 52, 7663 (1996).
65
J. Berthelot and M. Founier, J. Chem. Educ., 63, 1011 (1986); J. Berthelot, Y. Benammar, and C. Lange,
Tetrahedron Lett., 32, 4135 (1991).