Page 531 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 531
512 These fundamental aspects of epoxide ring opening were established by kinetic and
isotopic labeling studies. 159 The dominant role of bond cleavage in acidic hydrolysis
CHAPTER 5
is indicated by the increase in rates with additional substitution. Note in particular that
Polar Addition the 2,2-dimethyl derivative is much more reactive than the cis and trans disubstituted
and Elimination
Reactions derivative, as expected for an intermediate with carbocation character.
O O CH O CH 3 O
O 3
CH 3 CH 3 CH 3 CH 3 CH 3
6.3 x 10 –4 3.5 x 10 –3 7.7 x 10 –3 14.8 x 10 –3 3.3 x 10 –1
–1
k sec at H = 0
0
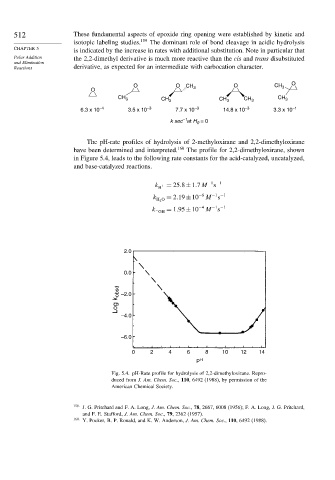
The pH-rate profiles of hydrolysis of 2-methyloxirane and 2,2-dimethyloxirane
have been determined and interpreted. 160 The profile for 2,2-dimethyloxirane, shown
in Figure 5.4, leads to the following rate constants for the acid-catalyzed, uncatalyzed,
and base-catalyzed reactions.
−1 −1
k + = 25 8±1 7M s
H
−1 −1
k H 2 O = 2 19±10 −6 M s
−1 −1
= 1 95±10 −4 M s
k− OH
2.0
0.0
Log k obsd –2.0
–4.0
–6.0
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14
P H
Fig. 5.4. pH-Rate profile for hydrolysis of 2,2-dimethyloxirane. Repro-
duced from J. Am. Chem. Soc., 110, 6492 (1988), by permission of the
American Chemical Society.
159 J. G. Pritchard and F. A. Long, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 78, 2667, 6008 (1956); F. A. Long, J. G. Pritchard,
and F. E. Stafford, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 79, 2362 (1957).
160
Y. Pocker, B. P. Ronald, and K. W. Anderson, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 110, 6492 (1988).