Page 578 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 578
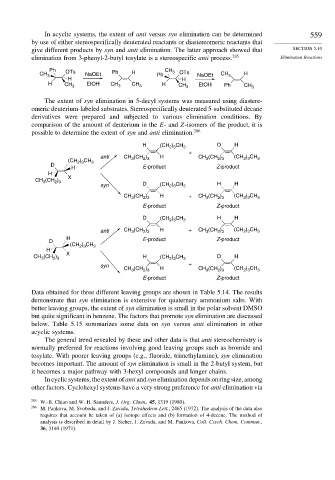
In acyclic systems, the extent of anti versus syn elimination can be determined 559
by use of either stereospecifically deuterated reactants or diastereomeric reactants that
give different products by syn and anti elimination. The latter approach showed that SECTION 5.10
elimination from 3-phenyl-2-butyl tosylate is a stereospecific anti process. 285 Elimination Reactions
Ph OTs CH 3 OTs
CH 3 NaOEt Ph H Ph NaOEt CH 3 H
H H
H CH 3 EtOH CH 3 CH 3 H CH 3 EtOH Ph CH 3
The extent of syn elimination in 5-decyl systems was measured using diastere-
omeric deuterium-labeled substrates. Stereospecifically deuterated 5-substituted decane
derivatives were prepared and subjected to various elimination conditions. By
comparison of the amount of deuterium in the E- and Z-isomers of the product, it is
possible to determine the extent of syn and anti elimination. 286
H (CH 2 3 3 D H
) CH
+
anti CH (CH ) H CH (CH ) (CH ) CH 3
2 3
(CH ) CH 3 3 2 3 3 2 3
2 3
D
H E-product Z-product
H
CH (CH ) X
3
2 3
syn D (CH ) CH 3 H H
2 3
CH (CH ) H + CH 3 (CH ) (CH ) CH 3
2 3
2 3
3
2 3
E-product Z-product
D (CH 2 3 3 H H
) CH
anti CH (CH ) H + CH (CH ) (CH ) CH 3
2 3
3
3
2 3
2 3
H
D E-product Z-product
(CH ) CH 3
2 3
H
CH (CH ) X H (CH 2 3 3 D H
) CH
2 3
3
syn +
CH (CH ) H CH (CH ) (CH ) CH 3
3
3
2 3
2 3
2 3
E-product Z-product
Data obtained for three different leaving groups are shown in Table 5.14. The results
demonstrate that syn elimination is extensive for quaternary ammonium salts. With
better leaving groups, the extent of syn elimination is small in the polar solvent DMSO
but quite significant in benzene. The factors that promote syn elimination are discussed
below. Table 5.15 summarizes some data on syn versus anti elimination in other
acyclic systems.
The general trend revealed by these and other data is that anti stereochemistry is
normally preferred for reactions involving good leaving groups such as bromide and
tosylate. With poorer leaving groups (e.g., fluoride, trimethylamine), syn elimination
becomes important. The amount of syn elimination is small in the 2-butyl system, but
it becomes a major pathway with 3-hexyl compounds and longer chains.
In cyclic systems, the extent of anti and syn elimination depends on ring size, among
other factors. Cyclohexyl systems have a very strong preference for anti elimination via
285 W.-B. Chiao and W. H. Saunders, J. Org. Chem., 45, 1319 (1980).
286
M. Pankova, M. Svoboda, and J. Zavada, Tetrahedron Lett., 2465 (1972). The analysis of the data also
requires that account be taken of (a) isotope effects and (b) formation of 4-decene. The method of
analysis is described in detail by J. Sicher, J. Zavada, and M. Pankova, Coll. Czech. Chem. Commun.,
36, 3140 (1971).