Page 579 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 579
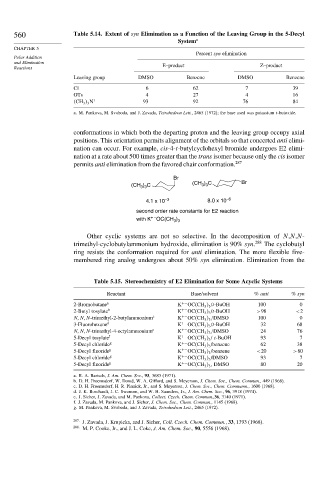
560 Table 5.14. Extent of syn Elimination as a Function of the Leaving Group in the 5-Decyl
System a
CHAPTER 5
Percent syn elimination
Polar Addition
and Elimination
Reactions E–product Z–product
Leaving group DMSO Benzene DMSO Benzene
Cl 6 62 7 39
OTs 4 27 4 16
CH 3 3 N + 93 92 76 84
a. M. Pankova, M. Svoboda, and J. Zavada, Tetrahedron Lett., 2465 (1972); the base used was potassium t-butoxide.
conformations in which both the departing proton and the leaving group occupy axial
positions. This orientation permits alignment of the orbitals so that concerted anti elimi-
nation can occur. For example, cis-4-t-butylcyclohexyl bromide undergoes E2 elimi-
nation at a rate about 500 times greater than the trans isomer because only the cis isomer
permits anti elimination from the favored chair conformation. 287
Br
) C
(CH ) C (CH 3 3 Br
3 3
4.1 x 10 –3 8.0 x 10 –6
second order rate constants for E2 reaction
with K + – OC(CH )
3 3
Other cyclic systems are not so selective. In the decomposition of N,N,N-
trimethyl-cyclobutylammonium hydroxide, elimination is 90% syn. 288 The cyclobutyl
ring resists the conformation required for anti elimination. The more flexible five-
membered ring analog undergoes about 50% syn elimination. Elimination from the
Table 5.15. Stereochemistry of E2 Elimination for Some Acyclic Systems
Reactant Base/solvent % anti % syn
2-Bromobutane a K +− OC CH 3 3 /t-BuOH 100 0
2-Butyl tosylate b K +− OC CH 3 3 /t-BuOH >98 <2
N N N-trimethyl-2-butylammonium c K +− OC CH 3 3 /DMSO 100 0
3-Fluorohexane d K +− OC CH 3 3 /t-BuOH 32 68
N N N-trimethyl-4-octylammonium e K +− OC CH 3 3 /DMSO 24 76
5-Decyl tosylate f K +− OC CH 3 3 / t-BuOH 93 7
5-Decyl chloride g K +− OC CH 3 3 /benzene 62 38
5-Decyl fluoride g K +− OC CH 3 3 /benzene <20 >80
5-Decyl chloride g K +− OC CH 3 3 /DMSO 93 7
5-Decyl fluoride g K +− OC CH 3 3 , DMSO 80 20
a. R. A. Bartsch, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 93, 3683 (1971).
b. D. H. Froemsdorf, W. Dowd, W. A. Gifford, and S. Meyerson, J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun., 449 (1968).
c. D. H. Froemsdorf, H. R. Pinnick, Jr., and S. Meyerson, J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commumn., 1600 (1968).
d. J. K. Borchardt, J. C. Swanson, and W. H. Saunders, Jr., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 96, 3918 (1974).
e. J. Sicher, J. Zavada, and M. Pankova, Collect. Czech. Chem. Commun.,36, 3140 (1971).
f. J. Zavada, M. Pankova, and J. Sicher, J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun., 1145 (1968).
g. M. Pankova, M. Svoboda, and J. Zavada, Tetrahedron Lett., 2465 (1972).
287 J. Zavada, J. Krupicka, and J. Sicher, Coll. Czech. Chem. Commun., 33, 1393 (1968).
288
M. P. Cooke, Jr., and J. L. Coke, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 90, 5556 (1968).