Page 615 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 615
597
Si
Si SECTION 6.3
Si N Li
N Si Carbanions Stabilized by
Functional Groups
H Li
N(C H )
2 5 3
O
CH3
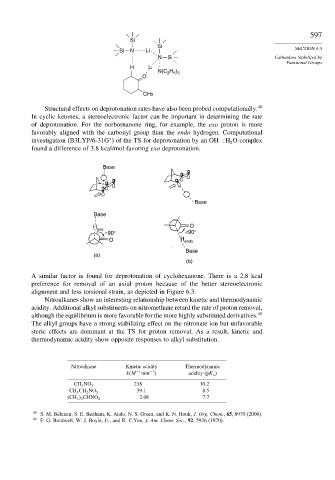
Structural effects on deprotonation rates have also been probed computationally. 48
In cyclic ketones, a stereoelectronic factor can be important in determining the rate
of deprotonation. For the norbornanone ring, for example, the exo proton is more
favorably aligned with the carbonyl group than the endo hydrogen. Computational
−
∗
investigation (B3LYP/6-31G ) of the TS for deprotonation by an OH H O complex
2
found a difference of 3.8 kcal/mol favoring exo deprotonation.
Base
Base
Base
H O
exo <90°
=90°
O H endo
Base
(a)
(b)
A similar factor is found for deprotonation of cyclohexanone. There is a 2.8 kcal
preference for removal of an axial proton because of the better stereoelectronic
alignment and less torsional strain, as depicted in Figure 6.3.
Nitroalkanes show an interesting relationship between kinetic and thermodynamic
acidity. Additional alkyl substituents on nitromethane retard the rate of proton removal,
although the equilibrium is more favorable for the more highly substituted derivatives. 49
The alkyl groups have a strong stabilizing effect on the nitronate ion but unfavorable
steric effects are dominant at the TS for proton removal. As a result, kinetic and
thermodynamic acidity show opposite responses to alkyl substitution.
Nitroalkane Kinetic acidity Thermodynamic
−1
k M −1 min acidity (pK a )
238 10 2
CH 3 NO 2
39 1 8 5
CH 3 CH 2 NO 2
2 08 7 7
CH 3 2 CHNO 2
48 S. M. Behnam, S. E. Benham, K. Ando, N. S. Green, and K. N. Houk, J. Org. Chem., 65, 8970 (2000).
49
F. G. Bordwell, W. J. Boyle, Jr., and K. C.Yee, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 92, 5926 (1970).