Page 619 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 619
are quite acidic. A series of aroylmethyl phosphonium ions has pK values of 4–7, with 601
the precise value depending on the aryl substituents. 58
SECTION 6.4
O O O – Enols and Enamines
+
+
X CCH 2 P Ph 3 X CCH – P Ph 3 X C CHP Ph 3
+
In the absence of the carbonyl or similar stabilizing group, the onium salts are less
acidic. The pK DMSO of methyltriphenylphosphonium ion is estimated to be 22. Strong
bases such as amide ion or the anion of DMSO are required to deprotonate alkylphos-
phonium salts.
strong
+
+
R CH P R' 3 base R C – P R' 3
2
2
Similar considerations apply to the sulfoxonium and sulfonium ylides, which are
formed by deprotonation of the corresponding positively charged sulfur-containing
cations. The additional electronegative oxygen atom in the sulfoxonium salts stabilizes
these ylides considerably, relative to the sulfonium ylides. 59
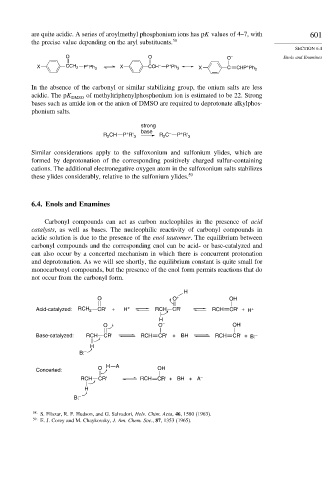
6.4. Enols and Enamines
Carbonyl compounds can act as carbon nucleophiles in the presence of acid
catalysts, as well as bases. The nucleophilic reactivity of carbonyl compounds in
acidic solution is due to the presence of the enol tautomer. The equilibrium between
carbonyl compounds and the corresponding enol can be acid- or base-catalyzed and
can also occur by a concerted mechanism in which there is concurrent protonation
and deprotonation. As we will see shortly, the equilibrium constant is quite small for
monocarbonyl compounds, but the presence of the enol form permits reactions that do
not occur from the carbonyl form.
H
O O + OH
Acid-catalyzed: RCH 2 CR' + H + RCH CR' RCH CR' + H +
H
O O – OH
Base-catalyzed: RCH CR' RCH CR' + BH RCH CR' + B: –
H
B: –
Concerted: O H A OH
–
RCH CR' RCH CR' + BH + A
H
B: –
58 S. Fliszar, R. F. Hudson, and G. Salvadori, Helv. Chim. Acta, 46, 1580 (1963).
59
E. J. Corey and M. Chaykovsky, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 87, 1353 (1965).