Page 738 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 738
13
1
The H and C shifts are also strongly dependent on carbon hybridization. In aromatic 721
compounds, the ring current makes a significant contribution to the overall chemical
26
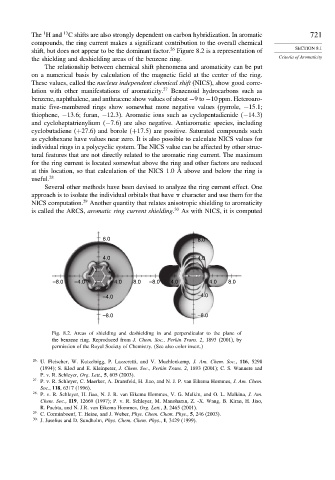
shift, but does not appear to be the dominant factor. Figure 8.2 is a representation of SECTION 8.1
the shielding and deshielding areas of the benzene ring. Criteria of Aromaticity
The relationship between chemical shift phenomena and aromaticity can be put
on a numerical basis by calculation of the magnetic field at the center of the ring.
These values, called the nucleus independent chemical shift (NICS), show good corre-
lation with other manifestations of aromaticity. 27 Benzenoid hydrocarbons such as
benzene, naphthalene, and anthracene show values of about −9to −10ppm. Heteroaro-
matic five-membered rings show somewhat more negative values (pyrrole, −15 1;
thiophene, −13 6; furan, −12 3). Aromatic ions such as cyclopentadienide (−14 3)
and cycloheptatrienylium (−7 6) are also negative. Antiaromatic species, including
cyclobutadiene (+27 6) and borole (+17 5) are positive. Saturated compounds such
as cyclohexane have values near zero. It is also possible to calculate NICS values for
individual rings in a polycyclic system. The NICS value can be affected by other struc-
tural features that are not directly related to the aromatic ring current. The maximum
for the ring current is located somewhat above the ring and other factors are reduced
at this location, so that calculation of the NICS 1.0 Å above and below the ring is
useful. 28
Several other methods have been devised to analyze the ring current effect. One
approach is to isolate the individual orbitals that have character and use them for the
29
NICS computation. Another quantity that relates anisotropic shielding to aromaticity
is called the ARCS, aromatic ring current shielding. 30 As with NICS, it is computed
8.0 8.0
4.0 4.0
–8.0 –4.0 4.0 8.0 –8.0 4.0 4.0 8.0
–4.0 –4.0
–8.0 –8.0
Fig. 8.2. Areas of shielding and deshielding in and perpendicular to the plane of
the benzene ring. Reproduced from J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 2, 1893 (2001), by
permission of the Royal Society of Chemistry. (See also color insert.)
26
U. Fleischer, W. Kutzelnigg, P. Lazzeretti, and V. Muehlenkamp, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 116, 5298
(1994); S. Klod and E. Kleinpeter, J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 2, 1893 (2001); C. S. Wannere and
P. v. R. Schleyer, Org. Lett., 5, 605 (2003).
27 P. v. R. Schleyer, C. Maerker, A. Dransfeld, H. Jiao, and N. J. P. van Eikema Hommes, J. Am. Chem.
Soc., 118, 6317 (1996).
28
P. v. R. Schleyer, H. Jiao, N. J. R. van Eikema Hommes, V. G. Malkin, and O. L. Malkina, J. Am.
Chem. Soc., 119, 12669 (1997); P. v. R. Schleyer, M. Manoharan, Z. -X. Wang, B. Kiran, H. Jiao,
R. Puchta, and N. J.R. van Eikema Hommes, Org. Lett., 3, 2465 (2001).
29 C. Corminboeuf, T. Heine, and J. Weber, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 5, 246 (2003).
30
J. Juselius and D. Sundholm, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 1, 3429 (1999).