Page 782 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 782
1
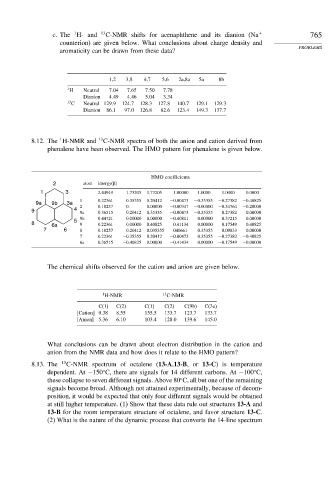
c. The H- and 13 C-NMR shifts for acenaphthene and its dianion (Na + 765
counterion) are given below. What conclusions about charge density and
PROBLEMS
aromaticity can be drawn from these data?
1,2 3,8 4,7 5,6 2a,8a 5a 8b
1 H Neutral 7 04 7 65 7 50 7 78
Dianion 4 49 4 46 5 04 3 34
13 C Neutral 129 9 124 7 128 3 127 8 140 7 129 1 129 3
Dianion 86 1 97 0 126 8 82 6 123 4 149 3 137 7
1
8.12. The H-NMR and 13 C-NMR spectra of both the anion and cation derived from
phenalene have been observed. The HMO pattern for phenalene is given below.
HMO coefficients
2 atom Energy( )
1 3 2.44949 1.73205 1.73205 1.00000 1.0000 1.0000 0.0000
1 0.22361 0.35355 0.20412 −0.00473 −0.35355 −0.27382 −0.40825
9a 9b 3a 2 0.18257 0. 0.00000 −0.00947 −0.00000 −0.54764 −0.20000
9 4 9a 0.36515 0.20412 0.35355 −0.00473 −0.35355 0.27382 0.00000
9b 0.44721 0.00000 0.00000 −0.40811 0.00000 0.37215 0.00000
5
8 6a 9 0.22361 −0.00000 0.40825 0.41134 0.00000 0.17549 0.40825
7 6 8 0.18257 −0.20412 0.035355 040661 0.35355 −0.09833 0.00000
7 0.22361 −0.35355 0.20412 −0.00473 0.35355 −0.27382 −0.40825
6a 0.36515 −0.40825 0.00000 −0.41434 0.00000 −0.17549 −0.00000
The chemical shifts observed for the cation and anion are given below.
1 H-NMR 13 C-NMR
C(1) C(2) C(1) C(2) C(9b) C(3a)
[Cation] 9.38 8.55 155.5 133.7 123.7 133.7
[Anion] 5.36 6.10 103.4 128.0 139.6 145.0
What conclusions can be drawn about electron distribution in the cation and
anion from the NMR data and how does it relate to the HMO pattern?
8.13. The 13 C-NMR spectrum of octalene (13-A,13-B,or 13-C) is temperature
dependent. At −150 C, there are signals for 14 different carbons. At −100 C,
these collapse to seven different signals. Above 80 C, all but one of the remaining
signals become broad. Although not attained experimentally, because of decom-
position, it would be expected that only four different signals would be obtained
at still higher temperature. (1) Show that these data rule out structures 13-A and
13-B for the room temperature structure of octalene, and favor structure 13-C.
(2) What is the nature of the dynamic process that converts the 14-line spectrum