Page 803 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 803
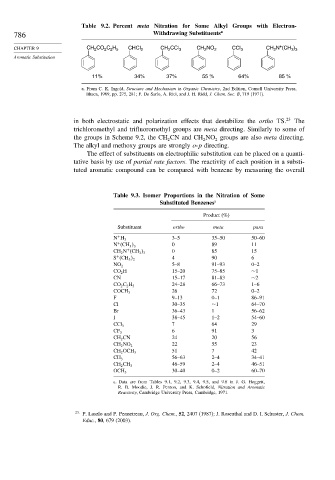
Table 9.2. Percent meta Nitration for Some Alkyl Groups with Electron-
786 Withdrawing Substituents a
+
CHAPTER 9 CH 2 CO 2 C 2 H 5 CHCl 2 CH 2 CCl 3 CH 2 NO 2 CCl 3 CH 2 N (CH 3 ) 3
Aromatic Substitution
11% 34% 37% 55 % 64% 85 %
a. From C. K. Ingold, Structure and Mechanism in Organic Chemistry, 2nd Edition, Cornell University Press,
Ithaca, 1969, pp. 275, 281; F. De Sarlo, A. Rici, and J. H. Ridd, J. Chem. Soc. B, 719 (1971).
in both electrostatic and polarization effects that destabilize the ortho TS. 23 The
trichloromethyl and trifluoromethyl groups are meta directing. Similarly to some of
the groups in Scheme 9.2, the CH CN and CH NO groups are also meta directing.
2
2
2
The alkyl and methoxy groups are strongly o-p directing.
The effect of substituents on electrophilic substitution can be placed on a quanti-
tative basis by use of partial rate factors. The reactivity of each position in a substi-
tuted aromatic compound can be compared with benzene by measuring the overall
Table 9.3. Isomer Proportions in the Nitration of Some
Substituted Benzenes a
Product (%)
Substituent ortho meta para
+ 3–5 35–50 50–60
N H 3
+ 0 89 11
N (CH 3 3
+ 0 85 15
CH 2 N (CH 3 3
+ 4 90 6
S (CH 3 2
5–8 91–93 0–2
NO 2
CO 2 H 15–20 75–85 ∼1
CN 15–17 81–83 ∼2
24–28 66–73 1–6
CO 2 C 2 H 5
26 72 0–2
COCH 3
F 9–13 0–1 86–91
Cl 30–35 ∼1 64–70
Br 36–43 1 56–62
I 38–45 1–2 54–60
7 64 29
CCl 3
6 91 3
CF 3
CH 2 CN 24 20 56
22 55 23
CH 2 NO 2
51 7 42
CH 2 OCH 3
56–63 2–4 34–41
CH 3
46–59 2–4 46–51
CH 2 CH 3
30–40 0–2 60–70
OCH 3
a. Data are from Tables 9.1, 9.2, 9.3, 9.4, 9.5, and 9.6 in J. G. Hoggett,
R. B. Moodie, J. R. Penton, and K. Schofield, Nitration and Aromatic
Reactivity, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1971.
23
P. Laszlo and P. Pennetreau, J. Org. Chem., 52, 2407 (1987); J. Rosenthal and D. I. Schuster, J. Chem.
Educ., 80, 679 (2003).