Page 1181 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part B - Reactions & Synthesis
P. 1181
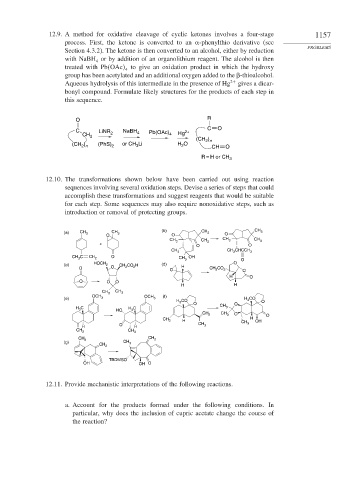
12.9. A method for oxidative cleavage of cyclic ketones involves a four-stage 1157
process. First, the ketone is converted to an -phenylthio derivative (see
PROBLEMS
Section 4.3.2). The ketone is then converted to an alcohol, either by reduction
with NaBH or by addition of an organolithium reagent. The alcohol is then
4
treated with Pb OAc to give an oxidation product in which the hydroxy
4
group has been acetylated and an additional oxygen added to the
-thioalcohol.
Aqueous hydrolysis of this intermediate in the presence of Hg 2+ gives a dicar-
bonyl compound. Formulate likely structures for the products of each step in
this sequence.
O R
C O
C LiNR 2 NaBH 4 Pb(OAc) 2+
CH 2 4 Hg
(CH )
2 n
) (PhS) or CH Li H O
(CH 2 n 2 3 2 CH O
R = H or CH 3
12.10. The transformations shown below have been carried out using reaction
sequences involving several oxidation steps. Devise a series of steps that could
accomplish these transformations and suggest reagents that would be suitable
for each step. Some sequences may also require nonoxidative steps, such as
introduction or removal of protecting groups.
(b) CH 3
(a) CH 3 CH 3 CH 3 O
O O
CH 3
CH 3 CH 3 CH 3
O O
CH 3 CH 3 CHCCH 3
CH 3 C CH 2 O OH
CH 3 O
(c) HOCH 2 CH 2 CO 2 H (d) H O
O O CH 3 CO 2
O O
H O
O O O
H H
CH 3 CH 3
(f)
OCH 3
(e) OCH 3 H 3 CO
H 3 CO O
O O
H 3 C H 3 C CH 3
HO
O
CH 2 CH 3 O
H
CH 3 H CH 3 OH
H O H CH 3
CH 2 CH 3
CH 3 CH 2
(g) CH 3
CH 2
TBDMSO
OH OH O
12.11. Provide mechanistic interpretations of the following reactions.
a. Account for the products formed under the following conditions. In
particular, why does the inclusion of cupric acetate change the course of
the reaction?