Page 128 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part B - Reactions & Synthesis
P. 128
100 E- and Z-silyl thioketene acetals give the 2,3-anti product. The 3,4-syn ratio is
50:1, and is consistent with the Felkin model. When this nucleophile reacts with
CHAPTER 2
2-benzyloxypropanal (Entry 8), a chelation product results. The facial selectivity with
Reactions of Carbon respect to the methyl group is now reversed. Both isomers of the silyl thioketene acetal
Nucleophiles with
Carbonyl Compounds give mainly the 2,3-syn-3,4-syn product. The ratio is higher than 30:1 for the Z-enolate
but only 3:1 for the E-enolate.
Sn O HO
H CH 3
H CH Ph
Ph 3 O
O H
H CH 3
CH 3 H H )
(CH ) C S OSiR 3 COSC(CH 3 3
3 3
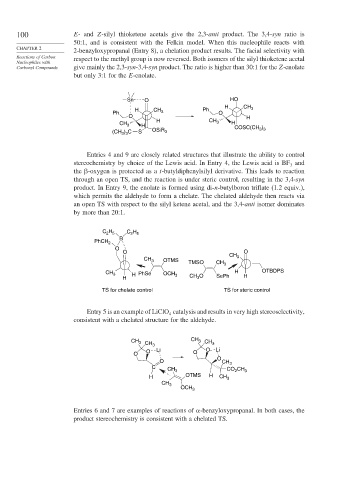
Entries 4 and 9 are closely related structures that illustrate the ability to control
stereochemistry by choice of the Lewis acid. In Entry 4, the Lewis acid is BF and
3
the -oxygen is protected as a t-butyldiphenylsilyl derivative. This leads to reaction
through an open TS, and the reaction is under steric control, resulting in the 3,4-syn
product. In Entry 9, the enolate is formed using di-n-butylboron triflate (1.2 equiv.),
which permits the aldehyde to form a chelate. The chelated aldehyde then reacts via
an open TS with respect to the silyl ketene acetal, and the 3,4-anti isomer dominates
by more than 20:1.
H
C 2 5 C H
2 5
B
PhCH 2
O
O CH O
CH 3 OTMS TMSO CH 3 3
CH 3 H PhSe OCH 3 O H OTBDPS
H CH 3 SePh H
TS for chelate control TS for steric control
Entry 5 is an example of LiClO catalysis and results in very high stereoselectivity,
4
consistent with a chelated structure for the aldehyde.
CH 3 CH CH 3 CH
3 3
O Li O O Li
O
O
O CH 3
C CH 3 CO CH 3
2
H OTMS H CH 3
CH 3
OCH 3
Entries 6 and 7 are examples of reactions of -benzyloxypropanal. In both cases, the
product stereochemistry is consistent with a chelated TS.