Page 227 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part B - Reactions & Synthesis
P. 227
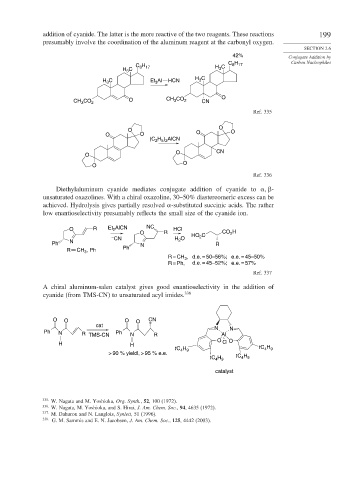
addition of cyanide. The latter is the more reactive of the two reagents. These reactions 199
presumably involve the coordination of the aluminum reagent at the carbonyl oxygen.
SECTION 2.6
42% Conjugate Addition by
H Carbon Nucleophiles
C 8 17
C 8 H 17 C
H C H 3
3
H C
H C Et Al HCN 3
3
3
CH CO 2 O CH CO 2 CN O
3
3
Ref. 335
O
O O O
O O
(C H ) AlCN
2 5 2
O CN
O
O
O
Ref. 336
Diethylaluminum cyanide mediates conjugate addition of cyanide to -
unsaturated oxazolines. With a chiral oxazoline, 30–50% diastereomeric excess can be
achieved. Hydrolysis gives partially resolved -substituted succinic acids. The rather
low enantioselectivity presumably reflects the small size of the cyanide ion.
O R Et 2 AlCN NC HCl
O R CO H
2
– CN H 2 O HO 2 C
Ph N N R
Ph
R CH , Ph
3
R = CH , d.e. = 50–56%; e.e. = 45–50%
3
R = Ph, d.e. = 45–52%; e.e. = 57%
Ref. 337
A chiral aluminum-salen catalyst gives good enantioselectivity in the addition of
cyanide (from TMS-CN) to unsaturated acyl imides. 338
O O O O CN
cat N
Ph N R TMS-CN Ph N R Al N
O O
H H Cl
t C H t C H
4 9
4 9
> 90 % yieldl, > 95 % e.e.
t C H t C H
4 9
4 9
catalyst
335
W. Nagata and M. Yoshioka, Org. Synth., 52, 100 (1972).
336
W. Nagata, M. Yoshioka, and S. Hirai, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 94, 4635 (1972).
337 M. Dahuron and N. Langlois, Synlett, 51 (1996).
338
G. M. Sammis and E. N. Jacobsen, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 125, 4442 (2003).