Page 561 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part B - Reactions & Synthesis
P. 561
6.2.3. Catalysis of 1,3-Dipolar Cycloaddition Reactions 535
The role of Lewis acid catalysts in 1,3-DCA reactions is similar to that SECTION 6.2
in D-A reactions. The catalysis results from a lowering of the LUMO energy 1,3-Dipolar
Cycloaddition Reactions
of the dipolarophile, which is analogous to the Lewis acid catalysis of D-A
reactions. The more organized TS, incorporating the metal ion and associated ligands,
then enforces a preferred orientation of the reagents. In contrast to the D-A reaction
involving hydrocarbon dienes, 1,3-DCA reactions may encounter competing complex-
ation at the 1,3-dipole. Lewis acid interaction with the 1,3-dipole is likely to be
detrimental if the dipole is the more nucleophilic component of the reaction. For
example, with nitrones and enones, formation of a Lewis acid adduct with the nitrone
in competition with the enone is detrimental. One approach to the need for selectivity
is to use highly substituted catalysts that are selective for the less-substituted reactant.
Bulky aryloxyaluminum compounds are excellent catalysts for nitrone cycloaddition
and also enhance regioselectivity. The reaction of diphenylnitrone with enones is
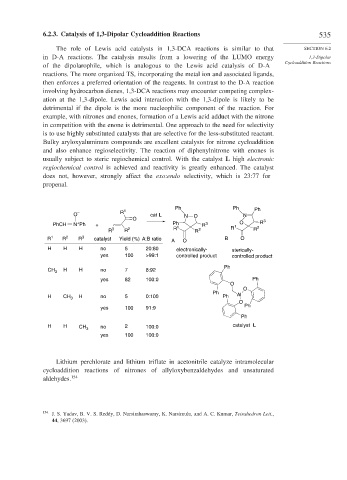
usually subject to steric regiochemical control. With the catalyst L high electronic
regiochemical control is achieved and reactivity is greatly enhanced. The catalyst
does not, however, strongly affect the exo:endo selectivity, which is 23:77 for
propenal.
Ph Ph Ph
1
O – R cat L N O N
O 3
+
PhCH N Ph + Ph 1 R 3 1 O R
R 3 R 2 R R 2 R R 2
R 1 R 2 R 3 catalyst Yield (%) A:B ratio A O B O
H H H no 5 20:80 electronically- sterically-
yes 100 >99:1 controlled product controlled product
Ph
CH 3 H H no 7 8:92
yes 82 100:0 Ph
O
O
Ph
H CH 3 H no 5 0:100 Ph Al
O
yes 100 91:9 Ph
Ph
H H CH 3 no 2 100:0 catalyst L
yes 100 100:0
Lithium perchlorate and lithium triflate in acetonitrile catalyze intramolecular
cycloaddition reactions of nitrones of allyloxybenzaldehydes and unsaturated
aldehydes. 154
154
J. S. Yadav, B. V. S. Reddy, D. Narsimhaswamy, K. Narsimulu, and A. C. Kumar, Tetrahedron Lett.,
44, 3697 (2003).