Page 564 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part B - Reactions & Synthesis
P. 564
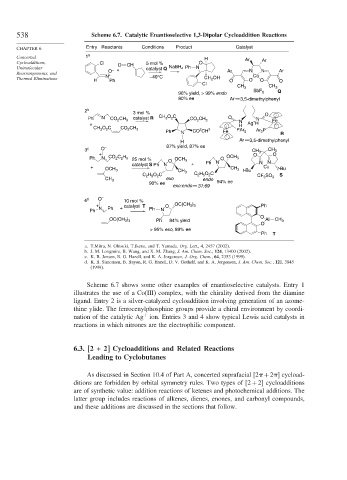
538 Scheme 6.7. Catalytic Enantioselective 1,3-Dipolar Cycloaddition Reactions
CHAPTER 6 Entry Reactants Conditions Product Catalyst
Concerted 1 a H Ar
Cycloadditions, Cl O CH 5 mol % O Ar
Unimolecular – + catalyst Q NaBH 4 Ph N N N Ar
Rearrangements, and O Ar Co
+
Thermal Eliminations H N Ph –40°C CH 2 OH O O O O
Cl
CH 3 CH 3
96% yield, > 99% endo SbF 6 Q
80% ee Ar 3,5-dimethylphenyl
2 b 3 mol % O
3
2
Ph N CO 2 CH 3 catalyst R CH O C CO CH 3 O N Fe
2
+
+ N Ag H
H
CH 3 O 2 C CO 2 CH 3 2 3 Ar 2 P
Ph N CO CH Fe PAr 2 R
H Ar 3,5-dimethylphenyl
3 c O – 87% yield, 87% ee CH 3 CH 3
+ O O
Ph N CO 2 C 2 H 5 25 mol % O OCH 3 O OCH 3
catalyst S Ph N + Ph N N N
+ Cu t -Bu
OCH 3 CH 3 t -Bu
CH 3
C 2 H 5 O 2 C C 2 H 5 O 2 C S
exo CF 3 SO 3
CH 3 endo
90% ee 94% ee
exo:endo 31:69
4 d O – 10 mol %
+ catalyst T O OC(CH 3 ) 3 Ph
Ph N Ph + Ph N
O
OC(CH 3 ) 3 Ph 84% yield Al CH 3
O
> 95% exo, 89% ee
Ph T
a. T.Mitra, N. Ohtsuki, T.Ikeno, and T. Yamada. Org. Lett., 4, 2457 (2002).
b. J. M. Longmire, B. Wang, and X. M. Zhang, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 124, 13400 (2002).
c. K. B. Jensen, R. G. Hazell, and K. A. Jorgensen, J. Org. Chem., 64, 2353 (1999).
d. K. B. Simonsen, B. Bayon, R. G. Hazell, D. V. Gothelf, and K. A. Jorgensen, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 121, 3845
(1999).
Scheme 6.7 shows some other examples of enantioselective catalysts. Entry 1
illustrates the use of a Co(III) complex, with the chirality derived from the diamine
ligand. Entry 2 is a silver-catalyzed cycloaddition involving generation of an azome-
thine ylide. The ferrocenylphosphine groups provide a chiral environment by coordi-
+
nation of the catalytic Ag ion. Entries 3 and 4 show typical Lewis acid catalysts in
reactions in which nitrones are the electrophilic component.
6.3. [2 + 2] Cycloadditions and Related Reactions
Leading to Cyclobutanes
As discussed in Section 10.4 of Part A, concerted suprafacial 2 +2 cycload-
ditions are forbidden by orbital symmetry rules. Two types of 2 +2 cycloadditions
are of synthetic value: addition reactions of ketenes and photochemical additions. The
latter group includes reactions of alkenes, dienes, enones, and carbonyl compounds,
and these additions are discussed in the sections that follow.