Page 634 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part B - Reactions & Synthesis
P. 634
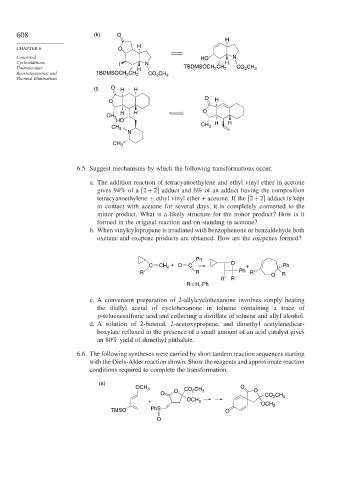
608 (k) O
H
H
CHAPTER 6 O
Concerted HO N
Cycloadditions, I N H
Unimolecular H TBDMSOCH CH 2 CO CH 3
2
2
Rearrangements, and TBDMSOCH 2 CH 2 CO 2 CH 3
Thermal Eliminations
(l) O H H
O
O H
H H O
CH 3
HO
CH H H
CH 3 3
N
CH 3
6.5. Suggest mechanisms by which the following transformations occur.
a. The addition reaction of tetracyanoethylene and ethyl vinyl ether in acetone
gives 94% of a 2 +2 adduct and 6% of an adduct having the composition
tetracyanoethylene + ethyl vinyl ether + acetone. If the 2+2 adduct is kept
in contact with acetone for several days, it is completely converted to the
minor product. What is a likely structure for the minor product? How is it
formed in the original reaction and on standing in acetone?
b. When vinylcylopropane is irradiated with benzophenone or benzaldehyde both
oxetane and oxepene products are obtained. How are the oxepenes formed?
Ph
C CH 2 + O C O + Ph
R′ R Ph R′ O R
R′ R
R = H, Ph
c. A convenient preparation of 2-allylcyclohexanone involves simply heating
the diallyl acetal of cyclohexanone in toluene containing a trace of
p-toluenesulfonic acid and collecting a distillate of toluene and allyl alcohol.
d. A solution of 2-butenal, 2-acetoxypropene, and dimethyl acetylenedicar-
boxylate refluxed in the presence of a small amount of an acid catalyst gives
an 80% yield of dimethyl phthalate.
6.6. The following syntheses were carried by short tandem reaction sequences starting
with the Diels-Alder reaction shown. Show the reagents and approximate reaction
conditions required to complete the transformation.
(a)
OCH 3 CO CH O O
O O 2 3 CO CH 3
2
+ OCH 3
OCH 3
TMSO PhS O
O