Page 77 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part B - Reactions & Synthesis
P. 77
49
SECTION 1.3
The Nitrogen Analogs of
Enols and Enolates:
Enamines
Li and Imine Anions
N
N
Li
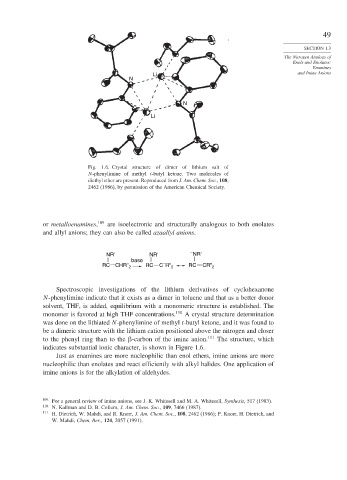
Fig. 1.6. Crystal structure of dimer of lithium salt of
N-phenylimine of methyl t-butyl ketone. Two molecules of
diethyl ether are present. Reproduced from J. Am. Chem. Soc., 108,
2462 (1986), by permission of the American Chemical Society.
or metalloenamines, 109 are isoelectronic and structurally analogous to both enolates
and allyl anions; they can also be called azaallyl anions.
–
NR' NR' NR'
base
–
RC CHR" 2 RC C R" 2 RC CR" 2
Spectroscopic investigations of the lithium derivatives of cyclohexanone
N-phenylimine indicate that it exists as a dimer in toluene and that as a better donor
solvent, THF, is added, equilibrium with a monomeric structure is established. The
monomer is favored at high THF concentrations. 110 A crystal structure determination
was done on the lithiated N-phenylimine of methyl t-butyl ketone, and it was found to
be a dimeric structure with the lithium cation positioned above the nitrogen and closer
to the phenyl ring than to the -carbon of the imine anion. 111 The structure, which
indicates substantial ionic character, is shown in Figure 1.6.
Just as enamines are more nucleophilic than enol ethers, imine anions are more
nucleophilic than enolates and react efficiently with alkyl halides. One application of
imine anions is for the alkylation of aldehydes.
109
For a general review of imine anions, see J. K. Whitesell and M. A. Whitesell, Synthesis, 517 (1983).
110 N. Kallman and D. B. Collum, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 109, 7466 (1987).
111
H. Dietrich, W. Mahdi, and R. Knorr, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 108, 2462 (1986); P. Knorr, H. Dietrich, and
W. Mahdi, Chem. Ber., 124, 2057 (1991).