Page 80 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part B - Reactions & Synthesis
P. 80
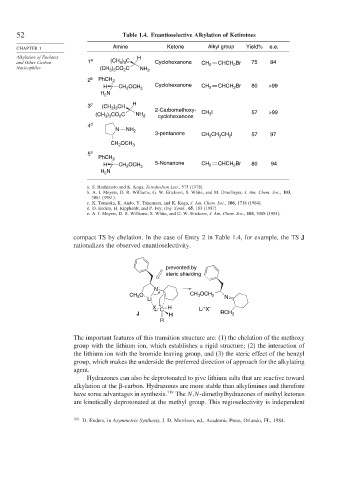
52 Table 1.4. Enantioselective Alkylation of Ketimines
CHAPTER 1 Amine Ketone Alkyl group Yield% e.e.
Alkylation of Enolates H
3 3
and Other Carbon 1 a (CH ) C Cyclohexanone CH 2 CHCH Br 75 84
2
Nucleophiles (CH ) CO C NH 2
3 3
2
2 b PhCH 2
H CH OCH 3 Cyclohexanone CH 2 CHCH Br 80 >99
2
2
N
H 2
3 c (CH ) CH H
3 3
2-Carbomethoxy-
3
(CH ) CO C NH 2 cyclohexanone CH I 57 >99
2
3 3
4 d
N NH 2
3-pentanone CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 I 57 97
CH OCH 3
2
5 e
PhCH 2
H CH OCH 3 5-Nonanone CH 2 CHCH Br 80 94
2
2
N
H 2
a. S. Hashimoto and K. Koga, Tetrahedron Lett., 573 (1978).
b. A. I. Meyers, D. R. Williams, G. W. Erickson, S. White, and M. Druelinger, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 103,
3081 (1981).
c. K. Tomioka, K. Ando, Y. Takemasa, and K. Koga, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 106, 1718 (1984).
d. D. Enders, H. Kipphardt, and P. Fey, Org. Synth., 65, 183 (1987).
e. A. I. Meyers, D. R. Williams, S. White, and G. W. Erickson, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 103, 3088 (1981).
compact TS by chelation. In the case of Entry 2 in Table 1.4, for example, the TS J
rationalizes the observed enantioselectivity.
prevented by
steric shielding
N
CH O CH OCH 2 N
3
3
Li
X C H Li X
+ –
J H RCH 2
R
The important features of this transition structure are: (1) the chelation of the methoxy
group with the lithium ion, which establishes a rigid structure; (2) the interaction of
the lithium ion with the bromide leaving group, and (3) the steric effect of the benzyl
group, which makes the underside the preferred direction of approach for the alkylating
agent.
Hydrazones can also be deprotonated to give lithium salts that are reactive toward
alkylation at the -carbon. Hydrazones are more stable than alkylimines and therefore
have some advantages in synthesis. 119 The N,N-dimethylhydrazones of methyl ketones
are kinetically deprotonated at the methyl group. This regioselectivity is independent
119
D. Enders, in Asymmetric Synthesis, J. D. Morrison, ed., Academic Press, Orlando, FL, 1984.