Page 879 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part B - Reactions & Synthesis
P. 879
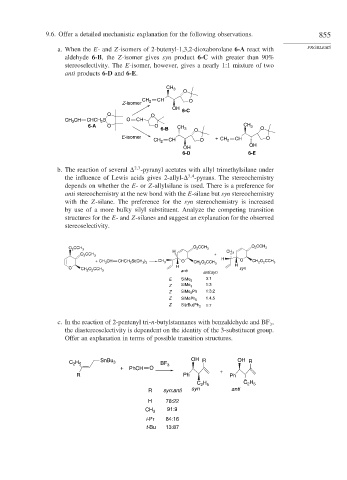
9.6. Offer a detailed mechanistic explanation for the following observations. 855
a. When the E- and Z-isomers of 2-butenyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolane 6-A react with PROBLEMS
aldehyde 6-B, the Z-isomer gives syn product 6-C with greater than 90%
stereoselectivity. The E-isomer, however, gives a nearly 1:1 mixture of two
anti products 6-D and 6-E.
CH 3
O
CH
CH 2 O
Z-isomer
OH
6-C
O O
CH 3 CH CHCH 2 B O CH
6-A O O CH 3
6-B CH 3 O O
E-isomer CH O
CH 2 CH O + CH 2
OH
OH
6-D 6-E
2
3
b. The reaction of several -pyranyl acetates with allyl trimethylsilane under
3
4
the influence of Lewis acids gives 2-allyl- -pyrans. The stereochemistry
depends on whether the E-or Z-allylsilane is used. There is a preference for
anti stereochemistry at the new bond with the E-silane but syn stereochemistry
with the Z-silane. The preference for the syn stereochemistry is increased
by use of a more bulky silyl substituent. Analyze the competing transition
structures for the E- and Z-silanes and suggest an explanation for the observed
stereoselectivity.
O 2 CCH 3
O 2 CCH 3 O 2 CCH 3
H CH 3
O 2 CCH 3 +
H
+ CH 3 CH CH 3 O O CH 2 O 2 CCH 3
CHCH 2 Si(CH 3 ) 3
CH 2 O 2 CCH 3
H H
O syn
CH 2 O 2 CCH 3
anti anti:syn
E SiMe 3 3:1
Z SiMe 3 1:3
Z SiMe 2 Ph 1:3.2
Z SiMePh 2 1.4.5
Z Si(t Bu)Ph 2 1:7
c. In the reaction of 2-pentenyl tri-n-butylstannanes with benzaldehyde and BF ,
3
the diastereoselectivity is dependent on the identity of the 3-substituent group.
Offer an explanation in terms of possible transition structures.
C H SnBu 3 BF 3 OH R OH R
2 5
+ PhCH O
R Ph + Ph
C H C H
2 5
2 5
R syn:anti syn anti
H 78:22
CH 3 91:9
i-Pr 84:16
t-Bu 13:87