Page 407 - Advanced thermodynamics for engineers
P. 407
17.2 SIMPLE GAS TURBINE CYCLE ANALYSIS 397
(b)
Maximum 3 5
Temperature, T 2
(a) temperature Q
Heater Heater 4
23 Q 23 Q 45
6
Q
1
4 4’
2 3 5 Power
C T T
Q
3
W net
1 4 6 2
p 1
i
Cooler
Entropy, S
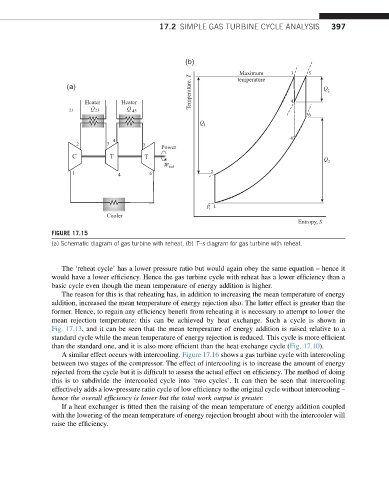
FIGURE 17.15
(a) Schematic diagram of gas turbine with reheat, (b) T–s diagram for gas turbine with reheat.
The ‘reheat cycle’ has a lower pressure ratio but would again obey the same equation – hence it
would have a lower efficiency. Hence the gas turbine cycle with reheat has a lower efficiency than a
basic cycle even though the mean temperature of energy addition is higher.
The reason for this is that reheating has, in addition to increasing the mean temperature of energy
addition, increased the mean temperature of energy rejection also. The latter effect is greater than the
former. Hence, to regain any efficiency benefit from reheating it is necessary to attempt to lower the
mean rejection temperature: this can be achieved by heat exchange. Such a cycle is shown in
Fig. 17.13, and it can be seen that the mean temperature of energy addition is raised relative to a
standard cycle while the mean temperature of energy rejection is reduced. This cycle is more efficient
than the standard one, and it is also more efficient than the heat exchange cycle (Fig. 17.10).
A similar effect occurs with intercooling. Figure 17.16 shows a gas turbine cycle with intercooling
between two stages of the compressor. The effect of intercooling is to increase the amount of energy
rejected from the cycle but it is difficult to assess the actual effect on efficiency. The method of doing
this is to subdivide the intercooled cycle into ‘two cycles’. It can then be seen that intercooling
effectively adds a low-pressure ratio cycle of low efficiency to the original cycle without intercooling –
hence the overall efficiency is lower but the total work output is greater.
If a heat exchanger is fitted then the raising of the mean temperature of energy addition coupled
with the lowering of the mean temperature of energy rejection brought about with the intercooler will
raise the efficiency.