Page 449 - Advanced thermodynamics for engineers
P. 449
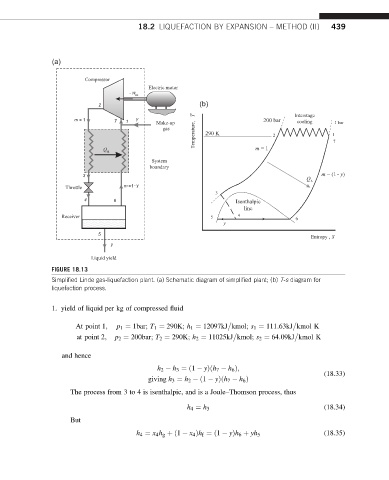
18.2 LIQUEFACTION BY EXPANSION – METHOD (II) 439
(a)
Compressor
Electric motor
- W in
2 (b)
T Interstage
m = 1 7 1 y Make-up 200 bar cooling 1 bar
Temperature, 290 K 2 1 7
gas
Q m = 1
A
System
boundary
3 m = (1- y)
Q
Throttle m = 1 - y
3
4 6 Isenthalpic
line
Receiver 5 4 6
y
5 Entropy , S
y
Liquid yield
FIGURE 18.13
Simplified Linde gas-liquefaction plant. (a) Schematic diagram of simplified plant; (b) T-s diagram for
liquefaction process.
1. yield of liquid per kg of compressed fluid
At point 1; p 1 ¼ 1bar; T 1 ¼ 290K; h 1 ¼ 12097kJ kmol; s 1 ¼ 111:63kJ kmol K
at point 2; p 2 ¼ 200bar; T 2 ¼ 290K; h 2 ¼ 11025kJ kmol; s 2 ¼ 64:09kJ kmol K
and hence
h 2 h 3 ¼ð1 yÞðh 7 h 6 Þ;
(18.33)
giving h 3 ¼ h 2 ð1 yÞðh 7 h 6 Þ
The process from 3 to 4 is isenthalpic, and is a Joule–Thomson process, thus
h 4 ¼ h 3 (18.34)
But
h 4 ¼ x 4 h g þð1 x 4 Þh f ¼ð1 yÞh 6 þ yh 5 (18.35)