Page 221 - Advances in Renewable Energies and Power Technologies
P. 221
194 CHAPTER 5 DMPPT PV System: Modeling and Control Techniques
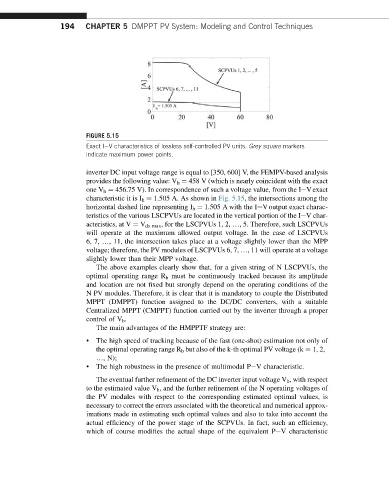
FIGURE 5.15
Exact IeV characteristics of lossless self-controlled PV units. Grey square markers
indicate maximum power points.
inverter DC input voltage range is equal to [350, 600] V, the FEMPV-based analysis
provides the following value: V h ¼ 458 V (which is nearly coincident with the exact
one V h ¼ 456.75 V). In correspondence of such a voltage value, from the IeVexact
characteristic it is I h ¼ 1.505 A. As shown in Fig. 5.15, the intersections among the
horizontal dashed line representing I h ¼ 1.505 A with the IeV output exact charac-
teristics of the various LSCPVUs are located in the vertical portion of the IeV char-
acteristics, at V ¼ V ds max , for the LSCPVUs 1, 2, ., 5. Therefore, such LSCPVUs
will operate at the maximum allowed output voltage. In the case of LSCPVUs
6, 7, ., 11, the intersection takes place at a voltage slightly lower than the MPP
voltage; therefore, the PV modules of LSCPVUs 6, 7, ., 11 will operate at a voltage
slightly lower than their MPP voltage.
The above examples clearly show that, for a given string of N LSCPVUs, the
optimal operating range R b must be continuously tracked because its amplitude
and location are not fixed but strongly depend on the operating conditions of the
N PV modules. Therefore, it is clear that it is mandatory to couple the Distributed
MPPT (DMPPT) function assigned to the DC/DC converters, with a suitable
Centralized MPPT (CMPPT) function carried out by the inverter through a proper
control of V b .
The main advantages of the HMPPTF strategy are:
• The high speed of tracking because of the fast (one-shot) estimation not only of
the optimal operating range R b but also of the k-th optimal PV voltage (k ¼ 1, 2,
.,N);
• The high robustness in the presence of multimodal PeV characteristic.
The eventual further refinement of the DC inverter input voltage V b , with respect
to the estimated value V h , and the further refinement of the N operating voltages of
the PV modules with respect to the corresponding estimated optimal values, is
necessary to correct the errors associated with the theoretical and numerical approx-
imations made in estimating such optimal values and also to take into account the
actual efficiency of the power stage of the SCPVUs. In fact, such an efficiency,
which of course modifies the actual shape of the equivalent PeV characteristic