Page 102 - Aircraft Stuctures for Engineering Student
P. 102
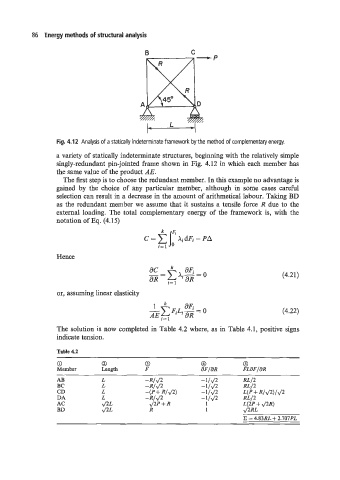
86 Energy methods of structural analysis
B C
Fig. 4.12 Analysis of a statically indeterminate framework by the method of complementary energy.
a variety of statically indeterminate structures, beginning with the relatively simple
singly-redundant pin-jointed frame shown in Fig. 4.12 in which each member has
the same value of the product AE.
The first step is to choose the redundant member. In this example no advantage is
gained by the choice of any particular member, although in some cases careful
selection can result in a decrease in the amount of arithmetical labour. Taking BD
as the redundant member we assume that it sustains a tensile force R due to the
external loading. The total complementary energy of the framework is, with the
notation of Eq. (4.15)
C = 21: AidFi - PA
i= 1
Hence
dFi
dC
- Ai - 0 (4.21)
=
=
dR . dR
1= 1
or, assuming linear elasticity
I k dFi
-E F ~ = o L ~ ~ (4.22)
AE.
1=1
The solution is now completed in Table 4.2 where, as in Table 4.1, positive signs
indicate tension.
Table 4.2
0 0 0
Member Length F