Page 400 - Aircraft Stuctures for Engineering Student
P. 400
10.3 Wings 381
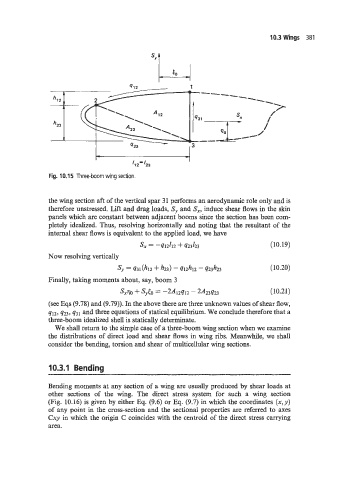
Fig. 10.15 Three-boorn wing section.
the wing section aft of the vertical spar 3 1 performs an aerodynamic role only and is
therefore unstressed. Lift and drag loads, S, and Sx, induce shear flows in the skin
panels which are constant between adjacent booms since the section has been com-
pletely idealized. Thus, resolving horizontally and noting that the resultant of the
internal shear flows is equivalent to the applied load, we have
sx = -412112 + q23l23 (10.19)
Now resolving vertically
sy = q31 (h12 + h23) - 412h12 - q23h23 (10.20)
Finally, taking moments about, say, boom 3
sxqO + sycO = -2A12q12 - 2A23q23 (10.21)
(see Eqs (9.78) and (9.79)). In the above there are three unknown values of shear flow,
q12, q23, q31 and three equations of statical equilibrium. We conclude therefore that a
three-boom idealized shell is statically determinate.
We shall return to the simple case of a three-boom wing section when we examine
the distributions of direct load and shear flows in wing ribs. Meanwhile, we shall
consider the bending, torsion and shear of multicellular wing sections.
10.3.1 Bending
w-111-w __II -_I__
Bending moments at any section of a wing are usually produced by shear loads at
other sections of the wing. The direct stress system for such a wing section
(Fig. 10.16) is given by either Eq. (9.6) or Eq. (9.7) in which the coordinates (x,y)
of any point in the cross-section and the sectional properties are referred to axes
Cxy in which the origin C coincides with the centroid of the direct stress carrying
area.