Page 581 -
P. 581
DECISION ANALYSIS WITH SAMPLE INFORMATION 561
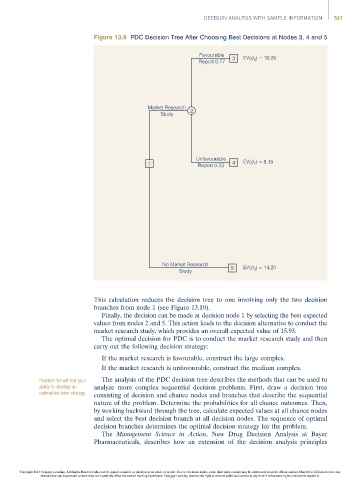
Figure 13.9 PDC Decision Tree After Choosing Best Decisions at Nodes 3, 4 and 5
Favourable EV(d ) = 18.26
Report 0.77 3 3
Market Research 2
Study
Unfavourable
1 Report 0.23 4 EV(d 2 ) = 8.15
No Market Research 5 ) = 14.20
Study EV(d 3
This calculation reduces the decision tree to one involving only the two decision
branches from node 1 (see Figure 13.10).
Finally, the decision can be made at decision node 1 by selecting the best expected
values from nodes 2 and 5. This action leads to the decision alternative to conduct the
market research study, which provides an overall expected value of 15.93.
The optimal decision for PDC is to conduct the market research study and then
carry out the following decision strategy:
If the market research is favourable, construct the large complex.
If the market research is unfavourable, construct the medium complex.
Problem 10 will test your The analysis of the PDC decision tree describes the methods that can be used to
ability to develop an analyze more complex sequential decision problems. First, draw a decision tree
optimal decision strategy. consisting of decision and chance nodes and branches that describe the sequential
nature of the problem. Determine the probabilities for all chance outcomes. Then,
by working backward through the tree, calculate expected values at all chance nodes
and select the best decision branch at all decision nodes. The sequence of optimal
decision branches determines the optimal decision strategy for the problem.
The Management Science in Action, New Drug Decision Analysis at Bayer
Pharmaceuticals, describes how an extension of the decision analysis principles
Copyright 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s). Editorial review has
deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.