Page 130 - An Introduction to Microelectromechanical Systems Engineering
P. 130
Sensors and Analysis Systems 109
The demonstrated specifications of the Delphi Delco sensor over the tempera-
ture range of –40° to +125ºC include a resolution of 0.5º/s over a bandwidth of
25 Hz, limited by noise in the electronic circuitry. The nonlinearity in a rate range of
±100 º/s is less than 0.2º/s. The sensor survives the standard automotive shock test: a
drop from a height of one meter. The specifications are adequate for most automo-
tive and consumer applications.
Angular-Rate Sensor from Silicon Sensing Systems
The CRS family of yaw-rate sensors from Silicon Sensing Systems, a joint venture
between BAE Systems of Plymouth, Devon, England, and Sumitomo Precision
Products Company of Japan, is aimed at commercial and automotive applications.
It also uses a vibratory ring shell similar to the sensor from Delphi Delco but differs
on the excitation and sense methods. Electric current loops in a magnetic field,
instead of electrostatic electrodes, excite the primary mode of resonance. These
same loops provide the sense signal to detect the angular position of the vibration
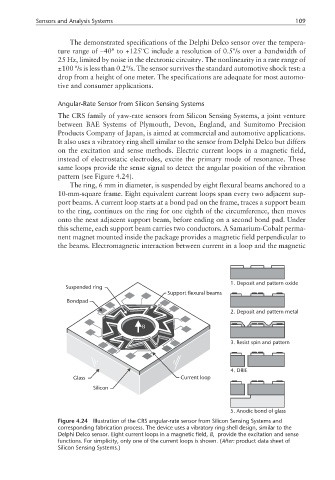
pattern (see Figure 4.24).
The ring, 6 mm in diameter, is suspended by eight flexural beams anchored to a
10-mm-square frame. Eight equivalent current loops span every two adjacent sup-
port beams. A current loop starts at a bond pad on the frame, traces a support beam
to the ring, continues on the ring for one eighth of the circumference, then moves
onto the next adjacent support beam, before ending on a second bond pad. Under
this scheme, each support beam carries two conductors. A Samarium-Cobalt perma-
nent magnet mounted inside the package provides a magnetic field perpendicular to
the beams. Electromagnetic interaction between current in a loop and the magnetic
1. Deposit and pattern oxide
Suspended ring
Support flexural beams
Bondpad
2. Deposit and pattern metal
B
3. Resist spin and pattern
4. DRIE
Glass Current loop
Silicon
5. Anodic bond of glass
Figure 4.24 Illustration of the CRS angular-rate sensor from Silicon Sensing Systems and
corresponding fabrication process. The device uses a vibratory ring shell design, similar to the
Delphi Delco sensor. Eight current loops in a magnetic field, B, provide the excitation and sense
functions. For simplicity, only one of the current loops is shown. (After: product data sheet of
Silicon Sensing Systems.)