Page 105 - Analytical Electrochemistry 2d Ed - Jospeh Wang
P. 105
90 CONTROLLED-POTENTIAL TECHNIQUES
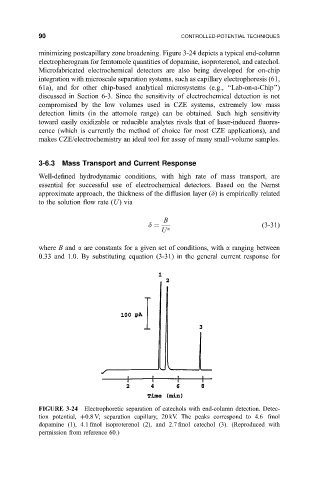
minimizing postcapillary zone broadening. Figure 3-24 depicts a typical end-column
electropherogram for femtomole quantities of dopamine, isoproterenol, and catechol.
Microfabricated electrochemical detectors are also being developed for on-chip
integration with microscale separation systems, such as capillary electrophoresis (61,
61a), and for other chip-based analytical microsystems (e.g., ``Lab-on-a-Chip'')
discussed in Section 6-3. Since the sensitivity of electrochemical detection is not
compromised by the low volumes used in CZE systems, extremely low mass
detection limits (in the attomole range) can be obtained. Such high sensitivity
toward easily oxidizable or reducible analytes rivals that of laser-induced ¯uores-
cence (which is currently the method of choice for most CZE applications), and
makes CZE/electrochemistry an ideal tool for assay of many small-volume samples.
3-6.3 Mass Transport and Current Response
Well-de®ned hydrodynamic conditions, with high rate of mass transport, are
essential for successful use of electrochemical detectors. Based on the Nernst
approximate approach, the thickness of the diffusion layer (d) is empirically related
to the solution ¯ow rate
U via
B
d a
3-31
U
where B and a are constants for a given set of conditions, with a ranging between
0.33 and 1.0. By substituting equation (3-31) in the general current response for
FIGURE 3-24 Electrophoretic separation of catechols with end-column detection. Detec-
tion potential, 0.8 V; separation capillary, 20 kV. The peaks correspond to 4.6 fmol
dopamine (1), 4.1 fmol isoproterenol (2), and 2.7 fmol catechol (3). (Reproduced with
permission from reference 60.)