Page 76 - Applied Process Design For Chemical And Petrochemical Plants Volume III
P. 76
66131_Ludwig_CH10B 5/30/2001 4:17 PM Page 54
54 Applied Process Design for Chemical and Petrochemical Plants
Table 10-11
Heat Exchange Operations
Equipment Designation Process Operation
Condenser (a) Condenses all vapors (pure or mixed) enter-
ing.
(b) Condenses all condensable vapor, cools
the gases—termed a cooler-condenser.
Partial Condenser Condenses only part of the total entering
vapors; condensed liquid removed as reflux or
as “fractionation mixture;” vapor passes out
unit to a second condenser, or on for other
processing.
Cooler Cools process stream, usually by water, but can
be by air as in air cooler or by other process
fluid.
Chiller Cools process stream by refrigerant at temper-
ature lower than prevailing water, can be
chilled by water cooling the process fluid or by
refrigerant such as ammonia, propylene, and
freon. (Also see “Evaporator.”)
Evaporator (a) Evaporates process fluid by some heating
medium such as steam.
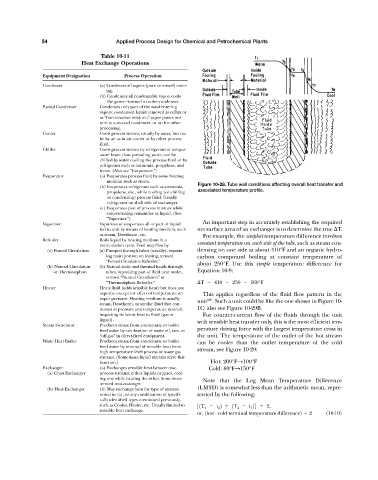
(b) Evaporates refrigerant such as ammonia, Figure 10-28. Tube wall conditions affecting overall heat transfer and
associated temperature profile.
propylene, etc., while cooling (or chilling
or condensing) process fluid. Usually
refrigerant on shell side of exchanger.
(c) Evaporates part of process mixture while
concentrating remainder as liquid. (See
“Vaporizer.”)
Vaporizer Vaporizes or evaporates all or part of liquid An important step in accurately establishing the required
fed to unit by means of heating medium, such net surface area of an exchanger is to determine the true T.
as steam, Dowtherm, etc. For example, the simplest temperature difference involves
Reboiler Boils liquid by heating medium in a
recirculation cycle. Feed may flow by constant temperature on each side of the tube, such as steam con-
(a) Forced Circulation (a) Pumped through tubes (usually), vaporiz- densing on one side at about 410°F and an organic hydro-
ing main portion on leaving, termed carbon compound boiling at constant temperature of
“Forced Circulation Reboiler.”
(b) Natural Circulation (b) Natural static and thermal heads through about 250°F. Use this simple temperature difference for
or Thermosiphon tubes, vaporizing part of fluid near outlet, Equation 10-9:
termed “Natural Circulation” or
“Thermosiphon Reboiler.” T 410 250 160°F
Heater Heats fluid (adds sensible heat) but does not
vaporize except for effect of temperature on This applies regardless of the fluid flow pattern in the
vapor pressure. Heating medium is usually 129
steam, Dowtherm, or similar fluid that con- unit . Such a unit could be like the one shown in Figure 10-
denses at pressure and temperature desired, 1C; also see Figure 10-29B.
imparting its latent heat to fluid (gas or For counter-current flow of the fluids through the unit
liquid). with sensible heat transfer only, this is the most efficient tem-
Steam Generator Produces steam from condensate or boiler
feed water by combustion of waste oil, tars, or perature driving force with the largest temperature cross in
“off-gas” in direct-fired equipment. the unit. The temperature of the outlet of the hot stream
Waste Heat Boiler Produces steam from condensate or boiler can be cooler than the outlet temperature of the cold
feed water by removal of sensible heat from
high temperature level process or waste gas stream, see Figure 10-29:
streams. (Sometimes liquid streams serve this
function.) Hot: 200°F→100°F
Exchanger (a) Exchanges sensible heat between two Cold: 80°F→150°F
(a) Cross Exchanger process streams, either liquids or gases, cool-
ing one while heating the other. Sometimes
Note that the Log Mean Temperature Difference
termed cross-exchanger.
(b) Heat-Exchanger (b) May exchange heat for type of streams (LMTD) is somewhat less than the arithmetic mean, repre-
noted in (a), or any combination of specifi- sented by the following:
cally identified types mentioned previously,
such as Cooler, Heater, etc. Usually limited to 31T 1 t 2 2 1T 2 t 1 24 2,
sensible heat exchange.
or, (hot - cold terminal temperature difference) 2 (10-10)