Page 222 -
P. 222
184 Part III Underbalanced Drilling Systems
Foam Drilling Model
Guo and colleagues’ foam drilling model (2003) is capable of simulating
gas, water, oil, and solid 4-phase flows. The model takes the same form as
Eq. (9.3). However, Eq. (9.11), derived for turbulent flow of aerated
liquids, is not valid for foam due to different flow regimes and rheological
models for foam. It can be shown that foams undergo laminar flows in
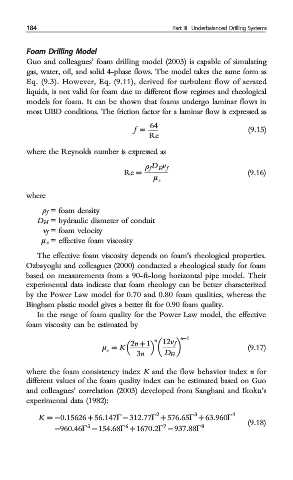
most UBD conditions. The friction factor for a laminar flow is expressed as
f = 64 (9.15)
Re
where the Reynolds number is expressed as
ρ D H v f
f
Re = (9.16)
μ e
where
ρ f = foam density
D H = hydraulic diameter of conduit
v f = foam velocity
μ e = effective foam viscosity
The effective foam viscosity depends on foam’s rheological properties.
Ozbayoglu and colleagues (2000) conducted a rheological study for foam
based on measurements from a 90-ft-long horizontal pipe model. Their
experimental data indicate that foam rheology can be better characterized
by the Power Law model for 0.70 and 0.80 foam qualities, whereas the
Bingham plastic model gives a better fit for 0.90 foam quality.
In the range of foam quality for the Power Law model, the effective
foam viscosity can be estimated by
n−1
2n + 1
n 12v f
μ = K (9.17)
e
3n D H
where the foam consistency index K and the flow behavior index n for
different values of the foam quality index can be estimated based on Guo
and colleagues’ correlation (2003) developed from Sanghani and Ikoku’s
experimental data (1982):
2
3
K = −0:15626 + 56:147Γ − 312:77Γ + 576:65Γ + 63:960Γ 4
(9.18)
−960:46Γ − 154:68Γ + 1670:2Γ − 937:88Γ 8
6
5
7