Page 466 - Applied Numerical Methods Using MATLAB
P. 466
PROBLEMS 455
(i) With the solution region divided into M × N = 100 × 100 sections,
2
2
what is the value of r = A( t) /( x) ?
(ii) Noting that the initial condition (P9.6.8) can be implemented by the
MATLAB statement as
>>it0 = inline(’(x-2).*(3-x).*(2<x&x<3)’,’x’);
solvethe PDE (P9.6.7) inthe same wayas in“solve_wave.m”and
make a dynamic picture out of the numerical solution, with the current
time printed on screen. Estimate the time when one of the two separated
pulses propagating leftwards is reflected and reversed. How about the
time when the two separated pulses are reunited?
9.7 FEM (Finite Element Method)
In expectation of better accuracy/resolution, modify the program
“do_fem.m” (in Section 9.6) by appending the following lines
;-17/32 -31/64; -1/2 -17/32;-15/32 -31/64
;17/32 31/64; 1/2 17/32; 15/32 31/64
to the last part of the Node array N and replacing the last line of the subregion
array S with
26 32 33; 27 33 34; 28 32 34; 29 35 36;
30 36 37; 31 35 37; 32 33 34; 35 36 37
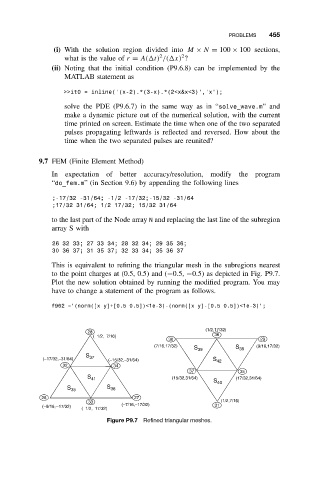
This is equivalent to refining the triangular mesh in the subregions nearest
to the point charges at (0.5, 0.5) and (−0.5, −0.5) as depicted in Fig. P9.7.
Plot the new solution obtained by running the modified program. You may
have to change a statement of the program as follows.
f962 =’(norm([x y]+[0.5 0.5])<1e-3)-(norm([x y]-[0.5 0.5])<1e-3)’;
(1/2,17/32)
28
(−1/2,−7/16) 36
30 29
(7/16,17/32) S 39 S 38 (9/16,17/32)
S
(−17/32,−31/64) 37 (−15/32,−31/64) S 42
32 34
37 35
S 41 (15/32,31/64) S 40 (17/32,31/64)
S 35 S 36
26 27
33 (1/2,7/16)
(−9/16,−17/32) (−7/16,−17/32) 31
(−1/2,−17/32)
Figure P9.7 Refined triangular meshes.