Page 68 - Applied Process Design For Chemical And Petrochemical Plants Volume II
P. 68
Distillation 57
V is an assumed or known value, based on reboiler independent of the mols of liquid water or organic com-
capacity. pound present. For example, for a system held at 800 mm
5. Plot of reflux quantity versus time. Hg, the mixture could boil at, say, 250°F, and both liquids
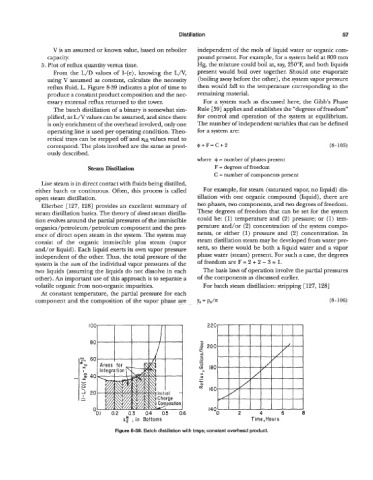
From the L/D values of 1-(e), knowing the L/V, present would boil over together. Should one evaporate
using V assumed as constant, calculate the necessity (boiling away before the other), the system vapor pressure
reflux fluid, L. Figure 8-39 indicates a plot of time to then would fall to the temperature corresponding to the
produce a constant product composition and the nec- remaining material.
essary external reflux returned to the tower. For a system such as discussed here, the Gibb’s Phase
The batch distillation of a binary is somewhat sim- Rule [59] applies and establishes the “degrees of freedom”
plified, as L/V values can be assumed, and since there for control and operation of the system at equilibrium.
is only enrichment of the overhead involved, only one The number of independent variables that can be defined
operating line is used per operating condition. Theo- for a system are:
retical trays can be stepped off and X~B values read to
correspond. The plots involved are the same as previ- 4+F-C+2 (8-105)
ously described.
where Q = number of phases present
Steam Distillation F = degrees of freedom
C = number of components present
Live steam is in direct contact with fluids being distilled,
either batch or continuous. Often, this process is called For example, for steam (saturated vapor, no liquid) dis-
open steam distillation. tillation with one organic compound (liquid), there are
Ellerbee [127, 1281 provides an excellent summary of two phases, two components, and two degrees of freedom.
steam distillation basics. The theory of direct steam distilla- These degrees of freedom that can be set for the system
tion evolves around the partial pressures of the immiscible could be: (I) temperature and (2) pressure; or (1) tem-
organics/petroleum/petroleum component and the pres- perature and/or (2) concentration of the system compo-
ence of direct open steam in the system. The system may nents, or either (I) pressure and (2) concentration. In
consist of the organic immiscible plus steam (vapor steam distillation steam may be developed from water pre-
and/or liquid). Each liquid exerts its own vapor pressure sent, so there would be both a liquid water and a vapor
independent of the other. Thus, the total pressure of the phase water (steam) present. For such a case, the degrees
system is the sum of the individual vapor pressures of the offreedom are F = 2 + 2 - 3 = 1.
two liquids (assuming the liquids do not dissolve in each The basis laws of operation involve the partial pressures
other). An important use of this approach is to separate a of the components as discussed earlier.
volatile organic from non-organic impurities. For batch steam distillation: stripping [127, 1281
At constant temperature, the partial pressure for each
component and the composition of the vapor phase are Ys = PSb (8-106)
”
0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6
x$ , in Bottoms Time, Hours
Figure 8-39. Batch distillation with trays; constant ovemead product.