Page 89 - Applied Statistics Using SPSS, STATISTICA, MATLAB and R
P. 89
68 2 Presenting and Summarising the Data
In multivariate problems, concerning datasets described by n random variables,
X 1, X 2, …, X n, one sometimes needs to assess what is the degree of association of
two variables, say X 1 and X 2, under the hypothesis that they are linearly estimated
by the remaining n – 2 variables. For this purpose, the correlation ρ X 1 X 2 is defined
in terms of the marginal distributions of X 1 or X 2 given the other variables, and is
then called the partial correlation of X 1 and X 2 given the other variables. Details on
partial correlations will be postponed to Chapter 7.
1.35 0.12
y y
1.30 0.10
1.25 0.08
1.20 0.06
1.15 0.04
1.10 0.02
1.05 0.00
1.00 -0.02
x x
a 0.95 -0.2 0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 1.2 b -0.04 -0.2 0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 1.2
1.2 1.2
y y
1.0 1.0
0.8 0.8
0.6 0.6
0.4 0.4
0.2 0.2
0.0 0.0
x x
c -0.2 -0.2 0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 1.2 d -0.2 1.0 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 2.0 2.2 2.4
1.2
y y
0.24
1.0
0.20
0.8
0.16
0.6
0.12
0.4
0.08
0.2
0.04
0.0
x 0.00 x
e -0.2 -0.2 0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 1.2 f -0.2 0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 1.2
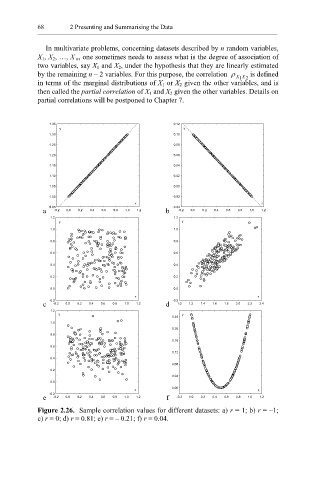
Figure 2.26. Sample correlation values for different datasets: a) r = 1; b) r = –1;
c) r = 0; d) r = 0.81; e) r = – 0.21; f) r = 0.04.