Page 144 - Arrow Pushing in Inorganic Chemistry A Logical Approach to the Chemistry of the Main Group Elements
P. 144
GROUP 14 ELEMENTS
124
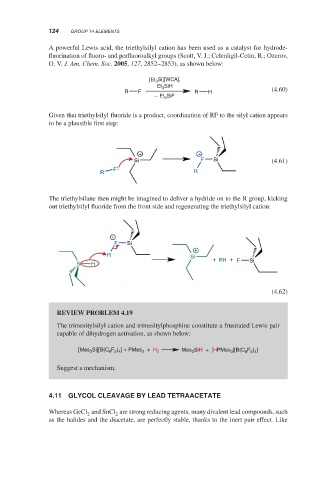
A powerful Lewis acid, the triethylsilyl cation has been used as a catalyst for hydrode-
fluorination of fluoro- and perfluoroalkyl groups (Scott, V. J.; Celenligil-Cetin, R.; Ozerov,
O. V. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 2852–2853), as shown below:
[Et 3 Si][WCA],
Et 3 SiH
R F R H (4.60)
− Et 3 SiF
Given that triethylsilyl fluoride is a product, coordination of RF to the silyl cation appears
to be a plausible first step:
+ +
Si F Si (4.61)
F
R R
The triethylsilane then might be imagined to deliver a hydride on to the R group, kicking
out triethylsilyl fluoride from the front side and regenerating the triethylsilyl cation:
+
F Si
+
R Si
+ RH + F Si
Si H
(4.62)
REVIEW PROBLEM 4.19
The trimesitylsilyl cation and trimesitylphosphine constitute a frustrated Lewis pair
capable of dihydrogen activation, as shown below:
[Mes Si][B(C F ) ] + PMes + H 2 Mes SiH + [HPMes ][B(C F ) ]
3
6 5 4
3
6 5 4
3
3
Suggest a mechanism.
4.11 GLYCOL CLEAVAGE BY LEAD TETRAACETATE
Whereas GeCl and SnCl are strong reducing agents, many divalent lead compounds, such
2
2
as the halides and the diacetate, are perfectly stable, thanks to the inert pair effect. Like