Page 241 - Arrow Pushing in Inorganic Chemistry A Logical Approach to the Chemistry of the Main Group Elements
P. 241
6.7 SULFUR OXOCHLORIDES 221
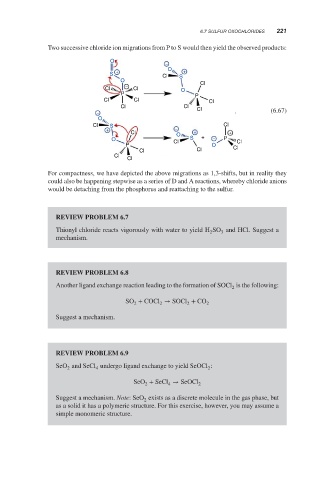
Two successive chloride ion migrations from P to S would then yield the observed products:
O
−
O
+ +
S Cl S
O Cl
−
Cl Cl O
P P
Cl Cl Cl
Cl Cl Cl
− (6.67)
O
Cl S Cl
+ −
Cl + +
O
O Cl S + − P Cl
P O Cl
Cl Cl
Cl
Cl
For compactness, we have depicted the above migrations as 1,3-shifts, but in reality they
could also be happening stepwise as a series of D and A reactions, whereby chloride anions
would be detaching from the phosphorus and reattaching to the sulfur.
REVIEW PROBLEM 6.7
Thionyl chloride reacts vigorously with water to yield H SO and HCl. Suggest a
2
3
mechanism.
REVIEW PROBLEM 6.8
Another ligand exchange reaction leading to the formation of SOCl is the following:
2
SO + COCl → SOCl + CO 2
2
2
2
Suggest a mechanism.
REVIEW PROBLEM 6.9
SeO and SeCl undergo ligand exchange to yield SeOCl :
2
4
2
SeO + SeCl → SeOCl 2
2
4
Suggest a mechanism. Note: SeO exists as a discrete molecule in the gas phase, but
2
as a solid it has a polymeric structure. For this exercise, however, you may assume a
simple monomeric structure.