Page 33 - Arrow Pushing in Inorganic Chemistry A Logical Approach to the Chemistry of the Main Group Elements
P. 33
1.6 THERMODYNAMIC CONTROL: BOND DISSOCIATION ENERGIES (BDEs) 13
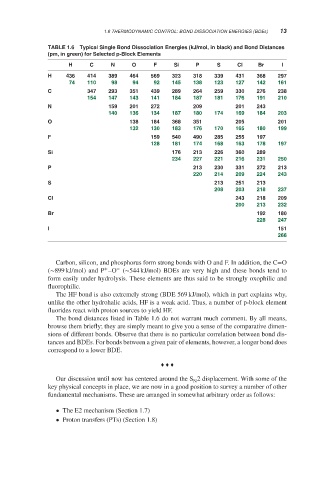
TABLE 1.6 Typical Single Bond Dissociation Energies (kJ/mol, in black) and Bond Distances
(pm, in green) for Selected p-Block Elements
H C N O F Si P S Cl Br I
H 436 414 389 464 569 323 318 339 431 368 297
110 98 92 145 138 123 127 142 161
74 94
C 347 293 351 439 289 264 259 330 276 238
147 143 141 187 181 176 191 210
154 184
N 159 201 272 209 201 243
140 136 134 187 180 174 169 184 203
O 138 184 368 351 205 201
132 130 183 176 170 165 180 199
F 159 540 490 285 255 197
128 181 174 168 163 178 197
Si 176 213 226 360 289
227 221 216 231 250
234
P 213 230 331 272 213
220 214 209 224 243
S 213 251 213
208 203 218 237
Cl 243 218 209
200 213 232
Br 192 180
228 247
I 151
266
Carbon, silicon, and phosphorus form strong bonds with O and F. In addition, the C=O
+ −
(∼899 kJ/mol) and P –O (∼544 kJ/mol) BDEs are very high and these bonds tend to
form easily under hydrolysis. These elements are thus said to be strongly oxophilic and
fluorophilic.
The HF bond is also extremely strong (BDE 569 kJ/mol), which in part explains why,
unlike the other hydrohalic acids, HF is a weak acid. Thus, a number of p-block element
fluorides react with proton sources to yield HF.
The bond distances listed in Table 1.6 do not warrant much comment. By all means,
browse them briefly; they are simply meant to give you a sense of the comparative dimen-
sions of different bonds. Observe that there is no particular correlation between bond dis-
tances and BDEs. For bonds between a given pair of elements, however, a longer bond does
correspond to a lower BDE.
♦♦♦
Our discussion until now has centered around the S 2 displacement. With some of the
N
key physical concepts in place, we are now in a good position to survey a number of other
fundamental mechanisms. These are arranged in somewhat arbitrary order as follows:
• The E2 mechanism (Section 1.7)
• Proton transfers (PTs) (Section 1.8)