Page 37 - Arrow Pushing in Inorganic Chemistry A Logical Approach to the Chemistry of the Main Group Elements
P. 37
1.9 ELEMENTARY ASSOCIATIVE AND DISSOCIATIVE PROCESSES (A AND D) 17
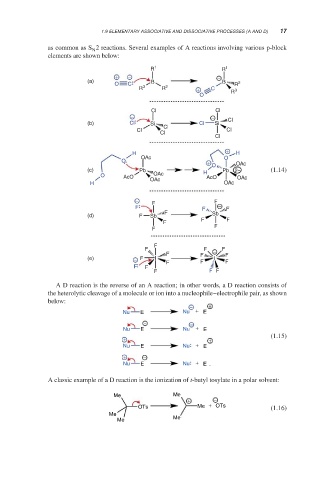
as common as S 2 reactions. Several examples of A reactions involving various p-block
N
elements are shown below:
R 1 R 1
+ − −
(a) B B
O C R 2
R 3 R 2 + C R 3
O
Cl Cl
− −
(b) Cl Si Cl Si Cl
Cl Cl Cl
Cl
Cl
+
H H
OAc O
O +
O OAc
(c) Pb H Pb 2− (1.14)
O AcO OAc AcO OAc
H OAc OAc
− F
F
F F − F
F Sb
(d) F Sb
F F
F
F F
F
F F − F
F F F
(e) − F I I
F F F
F F
F F F
A D reaction is the reverse of an A reaction; in other words, a D reaction consists of
the heterolytic cleavage of a molecule or ion into a nucleophile–electrophile pair, as shown
below:
− +
Nu E Nu + E
− −
Nu E Nu + E
(1.15)
+ +
Nu E Nu + E
+ −
Nu E Nu + E
A classic example of a D reaction is the ionization of t-butyl tosylate in a polar solvent:
Me Me
+ −
OTs Me + OTs (1.16)
Me
Me Me