Page 38 - Arrow Pushing in Inorganic Chemistry A Logical Approach to the Chemistry of the Main Group Elements
P. 38
A COLLECTION OF BASIC CONCEPTS
18
A more “inorganic” example might be the ionization of Martin sulfurane, a rather fancy
tetravalent-sulfur-based dehydrating agent (discussed in Section 6.13):
R F
O
Ph
Ph R F + Ph
S O − + S (1.17)
Ph
O O
R
R F F
A very common pathway for main-group elements is an A–D sequence. Thus, a nucleo-
phile and an electrophile come together to form a complex which then falls apart to a
different nucleophile–electrophile pair. The following fluoride ion transfer,
+
ClF + AsF → [ClF ] [AsF ] – (1.18)
3
6
2
5
a reaction typical of halogen fluorides, is a good example of the two-step process:
F
F
F
Cl
F Cl F F + F − F F −
F A F F D F F
F As As Cl + + As
F F F F F
F F F F
(1.19)
The D–A sequence is also fairly common. Possibly the best known example of such a
sequence is the S 1 pathway of organic chemistry, briefly described in the next section.
N
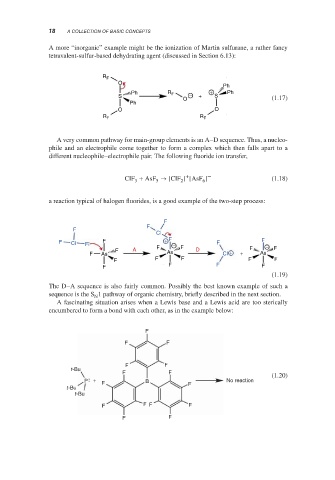
A fascinating situation arises when a Lewis base and a Lewis acid are too sterically
encumbered to form a bond with each other, as in the example below:
F
F F
F F
t-Bu
F F (1.20)
P + B No reaction
F F
t-Bu
t-Bu
F F F F
F F