Page 152 - Artificial Intelligence for Computational Modeling of the Heart
P. 152
124 Chapter 4 Data-driven reduction of cardiac models
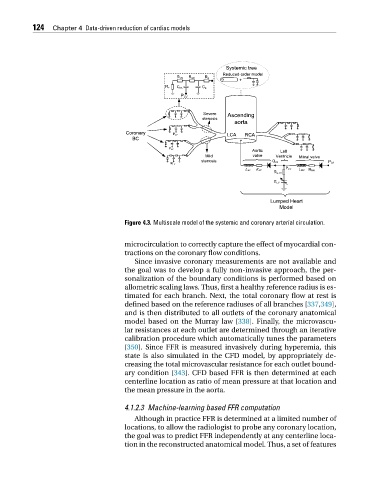
Figure 4.3. Multiscale model of the systemic and coronary arterial circulation.
microcirculation to correctly capture the effect of myocardial con-
tractions on the coronary flow conditions.
Since invasive coronary measurements are not available and
the goal was to develop a fully non-invasive approach, the per-
sonalization of the boundary conditions is performed based on
allometric scaling laws. Thus, first a healthy reference radius is es-
timated for each branch. Next, the total coronary flow at rest is
defined based on the reference radiuses of all branches [337,349],
and is then distributed to all outlets of the coronary anatomical
model based on the Murray law [338]. Finally, the microvascu-
lar resistances at each outlet are determined through an iterative
calibration procedure which automatically tunes the parameters
[350]. Since FFR is measured invasively during hyperemia, this
state is also simulated in the CFD model, by appropriately de-
creasing the total microvascular resistance for each outlet bound-
ary condition [343]. CFD based FFR is then determined at each
centerline location as ratio of mean pressure at that location and
the mean pressure in the aorta.
4.1.2.3 Machine-learning based FFR computation
Although in practice FFR is determined at a limited number of
locations, to allow the radiologist to probe any coronary location,
the goal was to predict FFR independently at any centerline loca-
tion in the reconstructed anatomical model. Thus, a set of features