Page 302 - Automotive Engineering Powertrain Chassis System and Vehicle Body
P. 302
Tyres and wheels C HAPTER 10.1
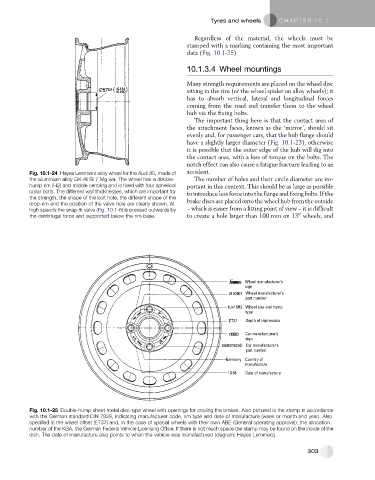
Regardless of the material, the wheels must be
stamped with a marking containing the most important
data (Fig. 10.1-25).
10.1.3.4 Wheel mountings
Many strength requirements are placed on the wheel disc
sitting in the rim (or the wheel spider on alloy wheels); it
has to absorb vertical, lateral and longitudinal forces
coming from the road and transfer them to the wheel
hub via the fixing bolts.
The important thing here is that the contact area of
the attachment faces, known as the ‘mirror’, should sit
evenly and, for passenger cars, that the hub flange should
have a slightly larger diameter (Fig. 10.1-23), otherwise
it is possible that the outer edge of the hub will dig into
the contact area, with a loss of torque on the bolts. The
notch effect can also cause a fatigue fracture leading to an
Fig. 10.1-24 Hayes Lemmerz alloy wheel for the Audi 80, made of accident.
the aluminium alloy GK-Al Si 7 Mg wa. The wheel has a double- The number of holes and their circle diameter are im-
hump rim (H2) and middle centring and is fixed with four spherical portant in this context. This should be as large as possible
collar bolts. The different wall thicknesses, which are important for tointroduceless force intotheflangeandfixing bolts.Ifthe
the strength, the shape of the bolt hole, the different shape of the brake discs are placed onto the wheel hub from the outside
drop-rim and the position of the valve hole are clearly shown. At
high speeds the snap-fit valve (Fig. 10.1-6) is pressed outwards by – which is easier from a fitting point of view – it is difficult
00
the centrifugal force and supported below the rim base. to create a hole larger than 100 mm on 13 wheels, and
Wheel manufacturer’s
sign
2150907 Wheel manufacturer’s
part number
6Jx15H2 Wheel size and hump
type
ET37 Depth of impression
Car manufacturer’s
sign
8A0601025G Car manufacturer’s
part number
Germany Country of
manufacture
10.98 Date of manufacture
Fig. 10.1-25 Double-hump sheet metal disc-type wheel with openings for cooling the brakes. Also pictured is the stamp in accordance
with the German standard DIN 7829, indicating manufacturer code, rim type and date of manufacture (week or month and year). Also
specified is the wheel offset (ET37) and, in the case of special wheels with their own ABE (General operating approval), the allocation
number of the KBA, the German Federal Vehicle Licensing Office. If there is not much space the stamp may be found on the inside of the
dish. The date of manufacture also points to when the vehicle was manufactured (diagram: Hayes Lemmerz).
303