Page 752 - Automotive Engineering Powertrain Chassis System and Vehicle Body
P. 752
Exterior noise: Assessment and control C HAPTER 22.1
90
80
70
60
SPL dB (lin) 50
40
30
20
10
0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000
Frequency (Hz)
Fig. 22.1-19 Sound pressure levels recorded 100 mm from the intake orifice of a 1.6-litre four-cylinder gasoline engine running full load at
1
2800 rev min .
22.1.3.12.2 Important design and development efficiently and then, selecting an appropriate expansion
parameters ratio for the silencer, determine the cross-sectional area
It is important to get the basic silencer expansion ratios of the silencer. The length of the silencer will depend on
and exhaust tailpipe (or snorkel) lengths right at the its position in the system (packaging considerations,
start of the design. It is not good practice to select a si- length of exhaust tailpipe required, etc.) and on the
lencer by volume. Rather, a designer should determine avoidance of critical resonant frequencies. These con-
the pipe diameter required to channel the flow siderations taken together determine the location and
90
80
70
60
SPL dB (lin) 50
40
30
20
10
0
0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000
Frequency (Hz)
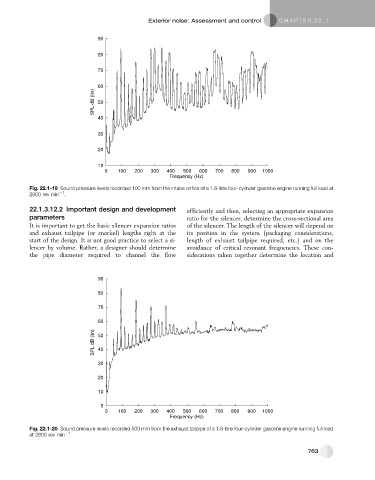
Fig. 22.1-20 Sound pressure levels recorded 500 mm from the exhaust tailpipe of a 1.6-litre four-cylinder gasoline engine running full load
1
at 2800 rev min .
763