Page 286 - Battery Reference Book
P. 286
Lithium-thionyl chloride primary batteries 2419
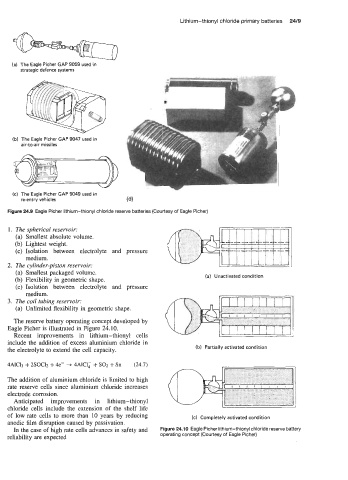
(a) The Eagle Picher GAP 9059 used in
strategic defence systems
(b) The Eagle Picher GAP 9047 used in
air-to-air missiles
(c) The Eagle Picher GAP 9049 used in
re-entry vehicles (a
Figure 24.9 Eagle Picher lithium-thionyl chloride reserve batteries (Courtesy of Eagle Picher)
1. The spherical reservoir:
(a) Smallest absolute volume.
(b) Lightest weight.
(c) Isolation between electrolyte and pressure
medium.
2. The cylinder-piston reservoir:
(a) Smallest packaged volume. (a) Unactivated condition
(b) Flexibility in geometric shape.
(c) Isolation between electrolyte and pressure
medium.
3. The coil tubing reservoir:
(a) Unlimited flexibility in geometric shape.
The reserve battery operating concept developed by
Eagle Picher is illustrated in Figure 24.10.
Recent improvements in lithium-thionyl cells
include the addition of excess aluminium chloride in
the electrolyte to extend the cell capacity. (b) Partially activated condition
4AlC13 + 2SOC12 + 4e- + 4AlCl; + SO2 + Sn (24.7)
The addition of aluminium chloride is limited to high
rate reserve cells since aluminium chloride increases
electrode corrosion.
Anticipated improvements in lithium-thionyl
chloride cells include the extension of the shelf life
of low rate cells to more than 10 years by reducing (c) Completely activated condition
anodic film disruption caused by passivation.
In the case of high rate cells advances in safety and Figure 24.10 Eagle Picher lithium-thionyl chloride reserve battery
reliability are expected operating concept (Courtesy of Eagle Picher)