Page 105 - Cascade_Biocatalysis_Integrating_Stereoselective_and_Environmentally_Friendly_Reactions
P. 105
4.3 Linear Cascade Reactions Involving ω-Transaminases 81
OH
O (R)-Selective ω-TA NH 2
OH Norpseudoephedrine
O AHAS-I OH ee > 99%
OH de > 98%
ThDP O (S)-Selective ω-TA
O CO 2 OH
(R)-PAC Alanine
98% ee
NH 2
Reversible O O O
acetolacetate formation AHAS-I Norephedrine
OH
OH ee > 99%
de > 98%
HO CO 2 O
Direct recycling Acetolactate
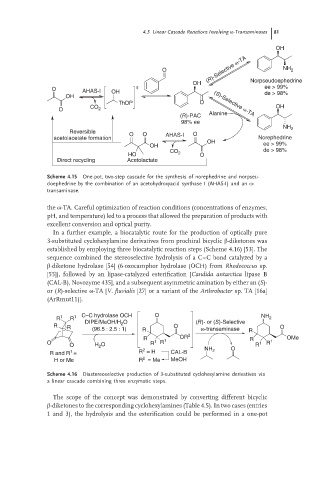
Scheme 4.15 One-pot, two-step cascade for the synthesis of norephedrine and norpseu-
doephedrine by the combination of an acetohydroxyacid synthase I (AHAS-I) and an ω-
transaminase.
the ω-TA. Careful optimization of reaction conditions (concentrations of enzymes,
pH, and temperature) led to a process that allowed the preparation of products with
excellent conversion and optical purity.
In a further example, a biocatalytic route for the production of optically pure
3-substituted cyclohexylamine derivatives from prochiral bicyclic β-diketones was
established by employing three biocatalytic reaction steps (Scheme 4.16) [53]. The
sequence combined the stereoselective hydrolysis of a C–C bond catalyzed by a
β-diketone hydrolase [54] (6-oxocamphor hydrolase (OCH) from Rhodococcus sp.
[55]), followed by an lipase-catalyzed esterification [Candida antarctica lipase B
(CAL-B), Novozyme 435], and a subsequent asymmetric amination by either an (S)-
or (R)-selective ω-TA [V. fluvialis [27] or a variant of the Arthrobacter sp. TA [16a]
(ArRmut11)].
R 1 R 1 C–C hydrolase OCH O NH 2
2
R R DIPE/MeOH/H O R O (R)- or (S)-Selective R O
(96.5 : 2.5 : 1)
ω-transaminase
R OR 2 R OMe
O O H O R 1 R 1 R 1 R 1
2
2
1
R and R = R = H CAL-B NH 2 O
2
H or Me R = Me MeOH
Scheme 4.16 Diastereoselective production of 3-substituted cyclohexylamine derivatives via
a linear cascade combining three enzymatic steps.
The scope of the concept was demonstrated by converting different bicyclic
β-diketones to the corresponding cyclohexylamines (Table 4.5). In two cases (entries
1 and 3), the hydrolysis and the esterification could be performed in a one-pot