Page 103 - Cascade_Biocatalysis_Integrating_Stereoselective_and_Environmentally_Friendly_Reactions
P. 103
4.3 Linear Cascade Reactions Involving ω-Transaminases 79
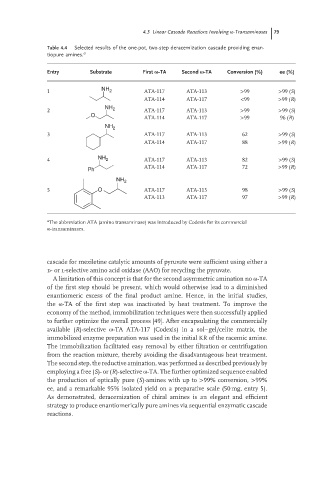
Table 4.4 Selected results of the one-pot, two-step deracemization cascade providing enan-
tiopure amines. a
Entry Substrate First -TA Second -TA Conversion (%) ee (%)
1 NH 2 ATA-117 ATA-113 >99 >99 (S)
ATA-114 ATA-117 <99 >99 (R)
NH
2 2 ATA-117 ATA-113 >99 >99 (S)
O
ATA-114 ATA-117 >99 96 (R)
NH 2
3 ATA-117 ATA-113 62 >99 (S)
ATA-114 ATA-117 88 >99 (R)
4 NH 2 ATA-117 ATA-113 82 >99 (S)
ATA-114 ATA-117 72 >99 (R)
Ph
NH 2
5 O ATA-117 ATA-113 98 >99 (S)
ATA-113 ATA-117 97 >99 (R)
a The abbreviation ATA (amino transaminase) was introduced by Codexis for its commercial
ω-transaminases.
cascade for mexiletine catalytic amounts of pyruvate were sufficient using either a
d-or l-selective amino acid oxidase (AAO) for recycling the pyruvate.
A limitation of this concept is that for the second asymmetric amination no ω-TA
of the first step should be present, which would otherwise lead to a diminished
enantiomeric excess of the final product amine. Hence, in the initial studies,
the ω-TA of the first step was inactivated by heat treatment. To improve the
economy of the method, immobilization techniques were then successfully applied
to further optimize the overall process [49]. After encapsulating the commercially
available (R)-selective ω-TA ATA-117 (Codexis) in a sol–gel/celite matrix, the
immobilized enzyme preparation was used in the initial KR of the racemic amine.
The immobilization facilitated easy removal by either filtration or centrifugation
from the reaction mixture, thereby avoiding the disadvantageous heat treatment.
The second step, the reductive amination, was performed as described previously by
employing a free (S)- or (R)-selective ω-TA. The further optimized sequence enabled
the production of optically pure (S)-amines with up to >99% conversion, >99%
ee, and a remarkable 95% isolated yield on a preparative scale (50 mg, entry 5).
As demonstrated, deracemization of chiral amines is an elegant and efficient
strategy to produce enantiomerically pure amines via sequential enzymatic cascade
reactions.