Page 99 - Cascade_Biocatalysis_Integrating_Stereoselective_and_Environmentally_Friendly_Reactions
P. 99
4.3 Linear Cascade Reactions Involving ω-Transaminases 75
transformation of easily available alcohols to the corresponding amines. Charac-
teristic features of these artificial networks include the versatility and flexibility of
the substrates, as also the high compatibility of the utilized enzymes. Moreover,
the possibility to define the stereochemial outcome of the product by the choice
of the employed ω-TA has opened a new pathway to a series of valuable secondary
amines under mild conditions.
4.3.2
Carbonyl Amination Followed by Spontaneous Ring Closure
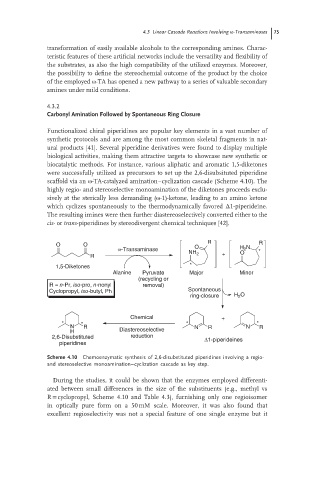
Functionalized chiral piperidines are popular key elements in a vast number of
synthetic protocols and are among the most common skeletal fragments in nat-
ural products [41]. Several piperidine derivatives were found to display multiple
biological activities, making them attractive targets to showcase new synthetic or
biocatalytic methods. For instance, various aliphatic and aromatic 1,5-diketones
were successfully utilized as precursors to set up the 2,6-disubsituted piperidine
scaffold via an ω-TA-catalyzed amination–cyclization cascade (Scheme 4.10). The
highly regio- and stereoselective monoamination of the diketones proceeds exclu-
sively at the sterically less demanding (ω-1)-ketone, leading to an amino ketone
which cyclizes spontaneously to the thermodynamically favored Δ1-piperideine.
The resulting imines were then further diastereoselectively converted either to the
cis-or trans-piperidines by stereodivergent chemical techniques [42].
R R
O O O H 2 N
ω-Transaminase *
NH 2 + O
R
1,5-Diketones *
Alanine Pyruvate Major Minor
(recycling or
R = n-Pr, iso-pro, n-nonyl removal)
Cyclopropyl, iso-butyl, Ph Spontaneous
ring-closure H 2 O
Chemical +
* * * *
N R N R N R
H Diastereoselective
2,6-Disubstituted reduction
Δ1-piperideines
piperidines
Scheme 4.10 Chemoenzymatic synthesis of 2,6-disubstituted piperidines involving a regio-
and stereoselective monoamination–cyclization cascade as key step.
During the studies, it could be shown that the enzymes employed differenti-
ated between small differences in the size of the substituents (e.g., methyl vs
R = cyclopropyl, Scheme 4.10 and Table 4.3), furnishing only one regioisomer
in optically pure form on a 50 mM scale. Moreover, it was also found that
excellent regioselectivity was not a special feature of one single enzyme but it