Page 95 - Cascade_Biocatalysis_Integrating_Stereoselective_and_Environmentally_Friendly_Reactions
P. 95
4.3 Linear Cascade Reactions Involving ω-Transaminases 71
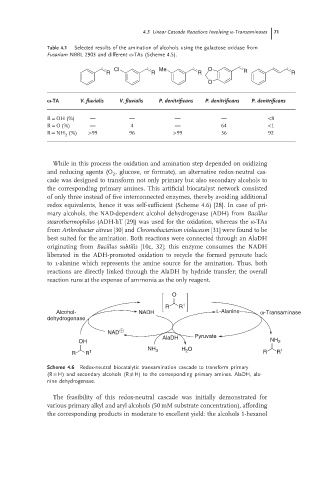
Table 4.1 Selected results of the amination of alcohols using the galactose oxidase from
Fusarium NRRL 2903 and different ω-TAs (Scheme 4.5).
Cl Me O
R R R R R
O
-TA V. fluvialis V. fluvialis P. denitrificans P. denitrificans P. denitrificans
R = OH (%) — — — — <8
R = O(%) — 4 — 64 <1
R = NH (%) >99 96 >99 36 92
2
While in this process the oxidation and amination step depended on oxidizing
and reducing agents (O , glucose, or formate), an alternative redox-neutral cas-
2
cade was designed to transform not only primary but also secondary alcohols to
the corresponding primary amines. This artificial biocatalyst network consisted
of only three instead of five interconnected enzymes, thereby avoiding additional
redox equivalents, hence it was self-sufficient (Scheme 4.6) [28]. In case of pri-
mary alcohols, the NAD-dependent alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) from Bacillus
stearothermophilus (ADH-hT [29]) was used for the oxidation, whereas the ω-TAs
from Arthrobacter citreus [30] and Chromobacterium violaceum [31] were found to be
best suited for the amination. Both reactions were connected through an AlaDH
originating from Bacillus subtilis [10c, 32]; this enzyme consumes the NADH
liberated in the ADH-promoted oxidation to recycle the formed pyruvate back
to l-alanine which represents the amine source for the amination. Thus, both
reactions are directly linked through the AlaDH by hydride transfer; the overall
reaction runs at the expense of ammonia as the only reagent.
O
R R 1
Alcohol- NADH L-Alanine ω-Transaminase
dehydrogenase
NAD
AlaDH Pyruvate
OH NH 2
NH 3 H O 1
R R 1 2 R R
Scheme 4.6 Redox-neutral biocatalytic transamination cascade to transform primary
(R = H) and secondary alcohols (R ≠ H) to the corresponding primary amines. AlaDH, ala-
nine dehydrogenase.
The feasibility of this redox-neutral cascade was initially demonstrated for
various primary alkyl and aryl alcohols (50 mM substrate concentration), affording
the corresponding products in moderate to excellent yield: the alcohols 1-hexanol