Page 100 - Cascade_Biocatalysis_Integrating_Stereoselective_and_Environmentally_Friendly_Reactions
P. 100
76 4 Biocatalytic Redox Cascades Involving -Transaminases
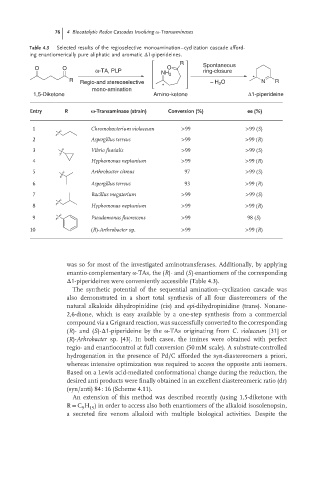
Table 4.3 Selected results of the regioselective monoamination–cyclization cascade afford-
ing enantiomerically pure aliphatic and aromatic Δ1-piperideines.
R Spontaneous
O O O
ω-TA, PLP ring-closure
NH 2
*
R Regio-and stereoselective − H 2 O N R
*
mono-amination
1,5-Diketone Amino-ketone Δ1-piperideine
Entry R -Transaminase (strain) Conversion (%) ee (%)
1 Chromobacterium violaceum >99 >99 (S)
2 Aspergillus terreus >99 >99 (R)
3 Vibrio fluvialis >99 >99 (S)
4 Hyphomonas neptunium >99 >99 (R)
5 Arthrobacter citreus 97 >99 (S)
6 Aspergillus terreus 93 >99 (R)
7 Bacillus megaterium >99 >99 (S)
8 Hyphomonas neptunium >99 >99 (R)
9 Pseudomonas fluorescens >99 98 (S)
10 (R)-Arthrobacter sp. >99 >99 (R)
was so for most of the investigated aminotransferases. Additionally, by applying
enantio-complementary ω-TAs, the (R)- and (S)-enantiomers of the corresponding
Δ1-piperideines were conveniently accessible (Table 4.3).
The synthetic potential of the sequential amination–cyclization cascade was
also demonstrated in a short total synthesis of all four diastereomers of the
natural alkaloids dihydropinidine (cis) and epi-dihydropinidine (trans). Nonane-
2,6-dione, which is easy available by a one-step synthesis from a commercial
compound via a Grignard reaction, was successfully converted to the corresponding
(R)- and (S)-Δ1-piperideine by the ω-TAs originating from C. violaceum [31] or
(R)-Arhrobacter sp. [43]. In both cases, the imines were obtained with perfect
regio- and enantiocontrol at full conversion (50 mM scale). A substrate-controlled
hydrogenation in the presence of Pd/C afforded the syn-diastereomers a priori,
whereas intensive optimization was required to access the opposite anti isomers.
Based on a Lewis acid-mediated conformational change during the reduction, the
desired anti products were finally obtained in an excellent diastereomeric ratio (dr)
(syn/anti) 84 : 16 (Scheme 4.11).
An extension of this method was described recently (using 1,5-diketone with
R = C H ) in order to access also both enantiomers of the alkaloid isosolenopsin,
9 19
a secreted fire venom alkaloid with multiple biological activities. Despite the