Page 102 - Cascade_Biocatalysis_Integrating_Stereoselective_and_Environmentally_Friendly_Reactions
P. 102
78 4 Biocatalytic Redox Cascades Involving -Transaminases
The transformation of the racemic aldehyde was investigated with various
commercially available ω-TAs in buffered solutions at various pH values and with
organic cosolvents as additives on a semipreparative scale (100 mg, 24 mM). Even
though almost full conversion was reported, the optically purity of the product was
only moderate at its best (68% ee). Nevertheless, the synthetic strategy is quite
general and allows obtaining optically enriched 4-arylpyrrolidin-2-one within only
three synthetic steps (54% overall yield), representing a significant improvement
compared to previous approaches.
4.3.3
Deracemization of Racemic Amines Employing Two -Transaminases
As already mentioned (Section 4.2), the ω-TA-catalyzed deracemization is a combi-
nation of a deamination with an asymmetric reductive amination. This technique
exploits the reversibility of ω-TA-catalyzed reaction, enabling the conversion of
a racemic mixture into a single enantiomer with a theoretical yield of 100%. In
general, an ideal KR (E > 100) of a racemic amine (first step) leads to a single amine
enantiomer in optically pure form (50%) and the corresponding prochiral ketone
(50%); the asymmetric amination of the intermediate ketone (second step) is then
catalyzed by a ω-TA, which is stereocomplementary to the first step. The two steps
are performed in a one-pot sequential cascade. Thus, in order to be able to produce
a single enantiomer starting from a racemic mixture, it is crucial to have access
to enzymes with opposite stereopreferences. Successful deracemization reactions
employing ω-TAs [47] were applied for the therapeutically relevant chiralamine mex-
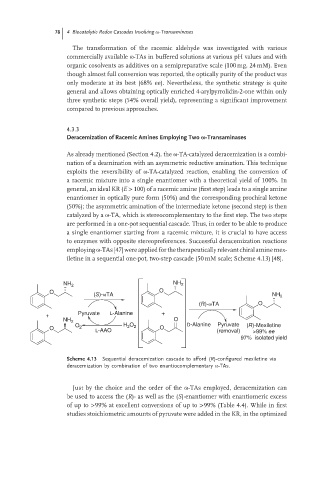
iletine in a sequential one-pot, two-step cascade (50 mM scale; Scheme 4.13) [48].
NH 2 NH 2
O O
(S)-ωTA NH 2
(R)-ωTA O
Pyruvate L-Alanine +
+
NH 2 O
Pyruvate
2
O O 2 L-AAO H O 2 O D-Alanine (removal) (R)-Mexiletine
>99% ee
97% isolated yield
Scheme 4.13 Sequential deracemization cascade to afford (R)-configured mexiletine via
deracemization by combination of two enantiocomplementary ω-TAs.
Just by the choice and the order of the ω-TAs employed, deracemization can
be used to access the (R)- as well as the (S)-enantiomer with enantiomeric excess
of up to >99% at excellent conversions of up to >99% (Table 4.4). While in first
studies stoichiometric amounts of pyruvate were added in the KR, in the optimized