Page 455 - Cascade_Biocatalysis_Integrating_Stereoselective_and_Environmentally_Friendly_Reactions
P. 455
19.3 Combination of Substrate Isomerization and their Derivatization 431
the desired alcohol (S)-6 with 96% conversion and 96% ee, thus indicating that
also palladium-catalyzed racemization was successful. Limitations of this process,
however, are the long reaction times (e.g., 19 days for the described example), the
deactivation of the palladium catalyst by some biocatalysts, and the low to medium
enantioselectivity for several substrates.
In addition to processes running in aqueous media, metal-catalyzed racemization
conducted in organic media has attracted attention as a valuable strategy for in
situ racemization of chiral organic molecules such as alcohols and amines. Such a
racemization is based on a reversible oxidation and reduction reaction of the chiral
alcohols and amines to ketones and imines as prochiral intermediates, respectively
[5–7]. Since lipases can also act as catalysts for enzymatic resolutions in organic
media, a combination of such a metal-catalyzed racemization and enzymatic
resolution then led to a DKR of racemic alcohols and amines. Pioneering work in
this field had also been done already in the 1990s by the Williams group jointly
with Harris [12] as well as the B¨ ackvall group [13, 14].
After screening a range of metal complexes based on iridium, aluminum,
rhodium, or ruthenium toward their suitability to racemize (S)-1-phenylethanol,
Williams and Harris et al. [12] demonstrated a proof of concept for the combination
of such a metal-catalyzed racemization of 1-phenylethanol with an in situ enzymatic
acylation of preferentially one enantiomer, although some limitations appeared
such as limited conversion and the need for a range of additives. A representative
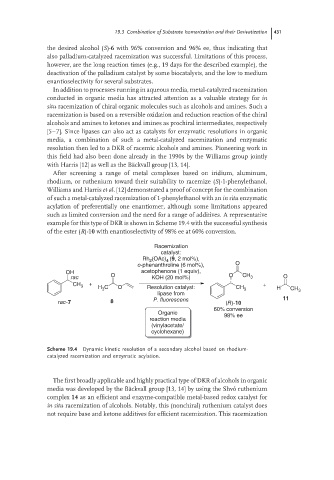
example for this type of DKR is shown in Scheme 19.4 with the successful synthesis
of the ester (R)-10 with enantioselectivity of 98% ee at 60% conversion.
Racemization
catalyst:
(OAc) (9, 2 mol%),
Rh 2 4
o-phenanthroline (6 mol%), O
OH acetophenone (1 equiv),
rac O KOH (20 mol%) O CH 3 O
CH 3 + H C O Resolution catalyst: CH + H CH
3
lipase from 3 3
rac-7 8 P. fluorescens (R)-10 11
60% conversion
Organic 98% ee
reaction media
(vinylacetate/
cyclohexane)
Scheme 19.4 Dynamic kinetic resolution of a secondary alcohol based on rhodium-
catalyzed racemization and enzymatic acylation.
The first broadly applicable and highly practical type of DKR of alcohols in organic
media was developed by the B¨ ackvall group [13, 14] by using the Shv´ o ruthenium
complex 14 as an efficient and enzyme-compatible metal-based redox catalyst for
in situ racemization of alcohols. Notably, this (nonchiral) ruthenium catalyst does
not require base and ketone additives for efficient racemization. This racemization