Page 460 - Cascade_Biocatalysis_Integrating_Stereoselective_and_Environmentally_Friendly_Reactions
P. 460
436 19 Chemoenzymatic Multistep One-Pot Processes
O
Lipase from
NH 2 C. antarctica B HN CH 3
(CAL-B)
CH 3
CH 3
EtOAc (2 equiv),
i-Pr 2 NEt, (R)-27
OH (R)-24 toluene >98% conversion
N
80% yield
Pd/C
Pd/C, H 2 98% ee
CH 3
Toluene
29 NH 2
CH 3
(S)-24
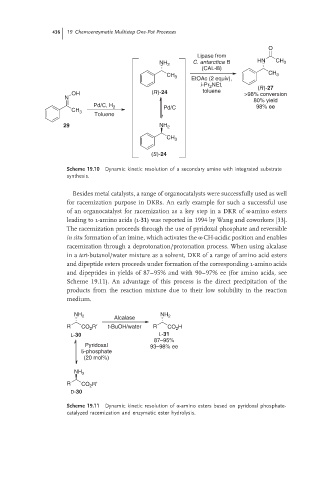
Scheme 19.10 Dynamic kinetic resolution of a secondary amine with integrated substrate
synthesis.
Besides metal catalysts, a range of organocatalysts were successfully used as well
for racemization purpose in DKRs. An early example for such a successful use
of an organocatalyst for racemization as a key step in a DKR of α-amino esters
leading to l-amino acids (l-31) was reported in 1994 by Wang and coworkers [33].
The racemization proceeds through the use of pyridoxal phosphate and reversible
in situ formation of an imine, which activates the α-CH-acidic position and enables
racemization through a deprotonation/protonation process. When using alcalase
in a tert-butanol/water mixture as a solvent, DKR of a range of amino acid esters
and dipeptide esters proceeds under formation of the corresponding l-amino acids
and dipeptides in yields of 87–95% and with 90–97% ee (for amino acids, see
Scheme 19.11). An advantage of this process is the direct precipitation of the
products from the reaction mixture due to their low solubility in the reaction
medium.
NH 2 Alcalase NH 2
R CO 2 R′ t-BuOH/water R CO 2 H
L-30 L-31
87–95%
Pyridoxal 93–98% ee
5-phosphate
(20 mol%)
NH 2
R CO R′
2
D-30
Scheme 19.11 Dynamic kinetic resolution of α-amino esters based on pyridoxal phosphate-
catalyzed racemization and enzymatic ester hydrolysis.